
Breastfeeding is an undoubted contribution to the health of the child. It’s good when it goes well, without complications. But no one is immune from such a nuisance as a lactation crisis. Even an experienced mother who has fed one baby may encounter this problem after the birth of the second. What factors affect lactation? How to avoid decreased milk production? How to improve the functioning of the mammary glands? Main conditions: balanced diet and daily routine.
With all the above benefits, encouragement breastfeeding and in particular, exclusive breastfeeding is considered one of the most cost-effective health strategies60. Exclusive breastfeeding rates are often much lower than overall breastfeeding rates, declining rapidly in the early postpartum days. Globally, less than half of children under four months of age receive breast milk as their sole source of water and food27.
In Latin America, only 20% of children under four months of age are exclusively breastfed. Data are available showing trends in exclusive breastfeeding practices for 42 countries45. It is growing in 22 countries, including Brazil, and declining in 7 countries. In other countries, rates remain stable.
After childbirth, a woman’s body functions under the influence of hormones. The mammary glands have their own mode of operation. During the first time after childbirth, colostrum is produced. This liquid differs from milk in its low fat and carbohydrate content, but surpasses it in the amount of protein, vitamins and antibodies that give the baby immune protection. Due to the fact that there is little colostrum, it resembles a lactation crisis. Not all mothers know what it is, only those who have encountered such an unpleasant phenomenon. Often in maternity hospitals, newborns are bottle-fed. This is unnecessary and can only cause harm. Colostrum is produced in small quantities, but it is quite enough to provide the baby with the necessary substances and enzymes. Excess fluid can literally wash away everything useful from the intestines. The newborn does not yet require large amounts of food.
Women with higher education breastfeed more. While for women with more than 12 years of education the average duration of exclusive breastfeeding was 2.1 months, for those with up to 3 years of education it was 0.6 months. Despite the importance of exclusive breastfeeding in the first 6 months for the health of a young child, few women practice it. Any attempt to increase breastfeeding rates must take into account factors that negatively influence the practice.
Because the recognition and definition of exclusive breastfeeding is relatively new, there is still a lot of confusion and misunderstanding about the importance of exclusive breastfeeding and its value. Although it is known that knowledge does not guarantee change in attitude, it is considered an important step in the process of behavior change37.
After 3 weeks, lactation usually enters a mature form. First the milk comes in, there is too much of it. Then the performance of the mammary glands and the baby's needs are coordinated, and he receives as much nutrition as he needs. After feeding, there is almost no milk left in the breast, but by the next feeding a sufficient amount has already formed.
Inadequate practice among health care professionals. Some practices medical workers may negatively impact establishment and maintenance of exclusive breastfeeding. Inadequate recommendations, lack of ability to support mothers who breastfeed, and inadequate clinical management are important barriers to exclusive breastfeeding.
Another problem with health care providers is the lack of clinical skills and breastfeeding counseling. Without these skills, health care professionals may not be able to properly assess breastfeeding to help women fully breastfeed and communicate effectively. In general, health care providers are not trained in breastfeeding counseling and practical aspects of lactation management during training. In addition, the lack of textbooks on the subject certainly contributes to the lack of knowledge and skills of health workers in the area of breastfeeding.
Any woman can experience a temporary decrease in milk production. Lactation is affected by nutrition, physical activity, and emotional state. Most often, a decrease in lactation occurs at 3-6 weeks and later - at 3, 4, 7 and 8 months. Perhaps there is no less milk, but the baby’s needs have increased. This is what happens most often. A lactation crisis may have some periodicity - about one and a half months. Usually this difficult period for mother and baby lasts 1-3 days. Sometimes you have to wait a week, but a lot depends on the woman’s mood. If she manages to pull herself together, feeding quickly returns to normal.
One study found that only 4 of 180 textbooks used in medical schools in 90 countries scored half or more of the maximum score for coverage of breastfeeding topics. 12 This study also found that textbooks rarely address practical breastfeeding management Maternal health.
Many culturally rooted beliefs and practices conflict with recommendations for optimal infant nutrition. In Brazil, one of them is adding water and tea. Teas are often introduced too early to quench a baby's thirst, soothe him, relieve colic, and treat various illnesses.
If the baby behaves restlessly during feeding, screams, and demands the breast again after a few minutes, the mother thinks that there is not enough milk. A baby’s anxiety can be caused by anything, it doesn’t have to be a lactation crisis. 3 months is the age when the baby may be bothered by colic, or he may be excited by some new events. If a woman feels that her breasts are constantly “empty,” this may be the main reason for crying. Don’t immediately get scared and assume that the milk is gone.
Most likely, the same amount is produced, the child simply strains out every drop. And this is the right behavior that will help overcome the lactation crisis. What should mom do? Allow the baby to fight for milk. The mechanism is very simple: the more he sucks, the faster everything will work out.
There is a relatively recent belief in many societies that breast milk alone is not sufficient to promote optimal growth of a child. As a consequence, types of milk other than mother's milk are introduced before the appropriate time. This practice may interfere with exclusive breastfeeding, as infants who use pacifiers tend to be more likely to get breastfeeding, 1, 69 which can interfere with milk production. It is possible that pacifier use is a marker of a mother's desire to stop breastfeeding earlier - as it reduces the frequency of breastfeeding rather than being a cause of interruption of lactation, especially in mothers with overt or hidden difficulties with breastfeeding.

A mother faced with a lack of milk needs to forget about other matters and take care of the child. He should receive breastfeeding upon request. Sucking gives a signal that there is not enough milk. This is the most effective stimulation of the mammary glands. If you initially feed on demand, you may not experience a lactation crisis. At 5 months, many mothers already strive to breastfeed hourly and only during the day. And this is a big mistake. It is at night that hormones responsible for lactation are produced. For successful feeding better for the baby sleep with mom. Close contact calms both and creates favorable conditions for milk production. Night feedings are mandatory when a lactation crisis occurs.
Breastfeeding and low self-esteem. 69. There is some evidence that bottle nozzles may have a negative effect on breastfeeding. It is difficult to distinguish the negative effect of a nipple from lactation from that of its contents. However, there is some evidence that the nozzles may have an independent effect. One study found that preterm infants or patients who received cup supplements were more likely to be breastfeeding exclusively at hospital discharge compared with infants who received a bottle40.
Many mothers notice that the baby remains dissatisfied with feeding, usually after active actions. For example, I played all evening with my dad and got overexcited. Mom was doing household chores at this time and was tired. As a result, the child wants to eat more, but produces less milk than usual. Often such everyday moments can explain a lactation crisis. What to do in this case? Just relax, lie in bed longer with your baby the next day. Just don’t worry, and you don’t have to immediately drink any decoctions or drugs to enhance lactation.
Although interference between pacifiers and bottle nozzles during exclusive breastfeeding has not been clearly established, it has been recommended that unnecessary use be avoided. 81. Misinterpretation of the behavior and normal needs of the newborn can be considered a cultural phenomenon. In societies where breastfeeding has been practiced at prearranged times for over a hundred years, there may have been changes in expectations about infant behavior. Thus, when a child frequently asks for the breast, it is common to interpret this human behavior as a consequence of insufficient or weak milk.
The mixture or just water will calm the baby. But just because he stops sucking persistently will not help increase milk production. Therefore, there is no need to rush. To make sure there is enough milk, you just need to count the wet diapers. If a child pees 12 times a day, there is no need to worry, he is not starving. Six wet diapers per day can be considered the norm. It is worth giving the mixture if periods of lactation crisis last longer than six days. It is better to feed not from a bottle, but from a spoon. 
Likewise, a baby's crying or fussing is usually interpreted as hunger, even in children who are growing properly. The child's non-nutritional needs, such as the desire to calm down, protection and relief from stress, are often ignored. 75. Although breastfeeding is a biologically determined process, it is highly dependent on the environment. And since this is not a completely instinctive act, it needs to be studied. Traditionally, more experienced women, usually members of the extended family, passed on their experience and supported new mothers, as well as helping them with household chores.
Doctors often recommend finding out how much milk the child drank at one time. Just one weighing may not be enough to make the right conclusion about your baby’s nutrition. His stomach is not designed for large volumes, his appetite differs at different times. With frequent feeding on demand, the child can drink 10 ml at one time, and 50 or 120 at the next dose. Therefore, you need to weigh the baby before and after feeding during the day.
Nowadays, in many modern societies this source of training and support has been lost as extended families have been replaced by nuclear families. As a consequence, women have little exposure to breastfeeding practices, resulting in them having inexperienced children who require constant encouragement and support from their families, health care providers and communities. When this support is insufficient, women easily lose confidence in their ability to fully breastfeed.
Perception of insufficient milk supply is a universal phenomenon, being the most common reason for early supplementation infant and interruption of breastfeeding in almost all societies. Most often, insufficient milk production is not just a perception resulting from mistrust, sometimes reinforced by family and friends in response to the baby's crying. Often, ineffective breastfeeding can result in an increased demand for the baby to breastfeed more frequently and for longer periods of time to produce sufficient milk.
To increase lactation, you can use the following methods. Before feeding, drink warm tea or milk 15-20 minutes before feeding, and arrange warm baths for the chest, arms and legs.
The total volume of liquid should be sufficient, but not too large. Excess water will not increase milk production, but will only create additional stress on the kidneys. Drink as much as you want.
Mothers of these children need help to breastfeed more effectively. 55. Transitional “crises” have been discovered during lactation, especially in the first months of the postpartum period. A Swedish study of 51 healthy infants found a 55% prevalence of poor milk acceptance, mainly due to emotional distress or refusal of breastfeeding31. This study confirms the ongoing need for support and encouragement for women who breastfeed so that there are fewer interruptions to exclusive breastfeeding due to transition crises.
A woman must be sure that breast milk is the best food for a child, that she is able and obliged to feed him, and no stress or obstacles can interfere with this. Doctors call this dominant lactation. If the mother initially feels confused and expects crises and other problems, most likely there will be them. Some women do not immediately begin to feed the child, citing sore nipples, for example, or coming up with other excuses. There is an opinion that lactation spoils the shape of the breast. This is not entirely true. Major changes occur during pregnancy. If a woman does not begin to breastfeed after childbirth, the mammary glands go through the involution stage within a month, colostrum never turns into mature milk and gradually disappears. But the shape of the breast does not improve. Therefore, you should not give up breastfeeding in hopes of an aesthetic effect.
Although studies in less developed countries indicate that maternal work is not the main reason for stopping breastfeeding and introducing breastfeeding, 67 it is known that maternal work may be a major barrier to breastfeeding in different populations. For example, in Brazil and Honduras, women who returned to work within the first 4 months after giving birth were less likely to breastfeed exclusively. 51 The relationship between maternal work and the duration and nature of breastfeeding depends on the type of occupation, working hours, 31 labor laws and support for breastfeeding in the work environment.
 Even during pregnancy, you need to set yourself up in a positive way. Of course, you should know in advance about possible difficulties, but you shouldn’t be afraid of them and wait for them at every step.
Even during pregnancy, you need to set yourself up in a positive way. Of course, you should know in advance about possible difficulties, but you shouldn’t be afraid of them and wait for them at every step.
In the future, you need to monitor your psychological state and not overwork. Those who do not get enough sleep are more likely to experience lactation crises. When you have sleepless nights, you need to rest during the day. Let someone else take care of the household chores. The mother's main job is to preserve milk.
It is very common for working babies to introduce breast milk substitutes very early in order to “wean” the baby. Additionally, there is insufficient knowledge among population and health professionals about breastfeeding management among working mothers to enable them to support successful breastfeeding.
Commercial promotion of formulas baby milk. A large amount of money is spent on commercial promotion of infant formula. The industry will not make such a large investment if advertising is not effective in increasing formula consumption. The International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes was adopted, which regulates the promotion of these substitutes and includes a ban on formula donations or subsidies to hospitals. Several studies have shown the negative impact of distributing samples to mothers in maternity hospitals.

The diet for breastfeeding women is not very different from the usual healthy diet. Lactation requires an additional 500-600 kcal per day, but this does not mean that you need to eat much more. A lactation crisis is often caused by poor nutrition. A balanced diet will help not only feed your baby for a long time, but also maintain health. During lactation, a woman should receive enough vitamins and minerals to provide enough for both her and her baby. You need to eat enough protein foods: meat, milk, fish. Vegetables such as carrots, pumpkin, lettuce, and radish have a beneficial effect on lactation. You can prepare decoctions and other healthy drinks from them. For example, fresh carrot juice with a little honey and cream.
A meta-analysis of 6 experimental studies found that mothers who received formula samples in the maternity ward were more likely to introduce formula in the first month and to stop breastfeeding after 4 months. 52. Therefore, although the actual impact of the implementation of the Code on breastfeeding rates is unknown, it is critical in the context of breastfeeding promotion.
The number of studies on the impact of interventions and programs on exceptional breastfeeding rates is still very limited. Among them, 11 involved health services, 3 were done with health promoters and 2 were done with community members. All but three studies were successful, increasing rates of exclusive breastfeeding. Table 1 presents the main characteristics, results and conclusions of the studies.
Nursing mothers should not eat smoked meats and marinades; the salt content in food should be minimal. Otherwise, fluid is retained in the body and milk production is reduced. An abundance of baked goods also has a bad effect on lactation. It is better to prefer bread with bran to baked goods.

Injury to the nipples or insufficient stimulation provoke lactation crises. When a mother experiences discomfort during feeding, she needs to make sure that the baby latches onto the breast correctly. The gums should not compress the nipple, but the areola. The nose touches the skin of the chest. If the latch is not deep enough, the baby constantly pulls at the nipple, this leads to cracks and has a bad effect on lactation in general. From the very beginning of feeding, you need to teach your baby to latch on to the breast correctly. If he has taken the nipple incorrectly, you should not simply pull it out of his mouth. First you need to carefully open your jaws by inserting your little finger between them. Then make sure that the child opens his mouth wide and apply again.

Of course, in some cases this requires a lot of patience. For example, if the nipples are flat, feeding is difficult. Often after the first attempts a woman despairs. In fact, a baby can suckle at any shape of breast. Only after feeding from a bottle will he not suffer from a “difficult” nipple or will not completely empty the breast. In such cases, milk stagnation or a lactation crisis usually develops.
At 3 months, the baby and mother are already accustomed to feeding and have learned everything. Other problems arise: some children like to play with the breast. They bite, pull the nipple between their tightly closed jaws, and the older ones can even roll the car while they eat. It is clear that such pampering does not bring any benefit, but only irritates the mother. Therefore, at the first pranks, you need to stop them and avoid neglectful treatment of your breasts. It is worth explaining to the child that mom is in pain, let him follow the rules.
Any way to improve a woman's health is useful for successful lactation. Massage also calms the nervous system. Improved blood circulation helps increase milk production. You can do any exercise that tightens your chest muscles. You need to massage with light strokes from the edge of the mammary glands to the nipples in a spiral. Massage of the thoracic region and collar area is useful.
Involution of the mammary glands occurs when a woman decides to stop feeding. A lactation crisis is sometimes frightening, it seems that the milk has disappeared. But, as noted earlier, you need to continue feeding, and there will be more milk. A sudden cessation of its production is possible only due to severe stress or hormonal imbalances. If feedings occur on demand, usually even after a year the baby has enough milk. When mom decides it's time to stop breastfeeding, the first thing she should do is feed by the hour. We can say that it artificially creates a lactation crisis. 3 months is the minimum period for weaning a child. The feeding schedule means that the baby no longer receives milk on demand. Then the number of applications per day decreases. Accordingly, milk production decreases. This process should be gradual and natural. If milk has accumulated in your breasts, you can deviate a little from the plan and feed the baby. If he didn’t wait until the evening feeding and fell asleep, that’s also good. Don’t forget that giving up breastfeeding is a step towards the baby’s independence and adulthood.
You can completely do without crises during lactation. You just need to maintain a healthy daily routine, eliminate bad habits, don’t be nervous and take care of your baby.
A lactation crisis is an insufficient production of milk by the mammary glands during lactation, which is transient in nature, appears for no apparent reason and ends on its own for no reason.
Lactation crises are normal physiological processes, as they are the result of hormonal changes in the body of a woman who has given birth - the production of the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for the formation of milk, decreases, and the child’s need for food increases.
Lactation crises occur:
The duration of the lactation crisis is 3-4 days (in some cases up to 7 days), then milk production is restored and the process returns to normal.

Fatigue and stress of a young mother aggravate the course of lactation crises and contribute to a decrease in her milk supply.
First of all, the appearance of a lactation crisis is influenced by the lack of a woman’s psychological attitude towards. Many mothers have heard from friends about lactation crises; as a result, they begin to fear that the milk will disappear and the baby will remain hungry; the resulting stress worsens the process of milk production.
In any case, the following negative factors influence a decrease in lactation:
The mother makes hasty conclusions that she does not have enough milk if her breasts did not enlarge during pregnancy, if milk did not arrive after childbirth, if when expressing there is no milk at all or it flows out in a single thin stream, if the child cries often and his mother often is breastfeeding, but the baby does not receive satisfaction from feeding, or the child has rare stools in small volumes.
All these signs are only a certain probability that there is really little milk. There are only three reliable signs of decreased milk supply:
On a note! There are no more than 3-5% of women in the world who actually produce insufficient milk. The remaining 97% of women quit breastfeeding due to their personal reluctance or lack of knowledge about the correct breastfeeding technique.
A temporary decrease in lactation for 3-7 days, i.e., a lactation crisis, does not harm the child, since this food unloading is a physiologically necessary phenomenon for an immature organism.
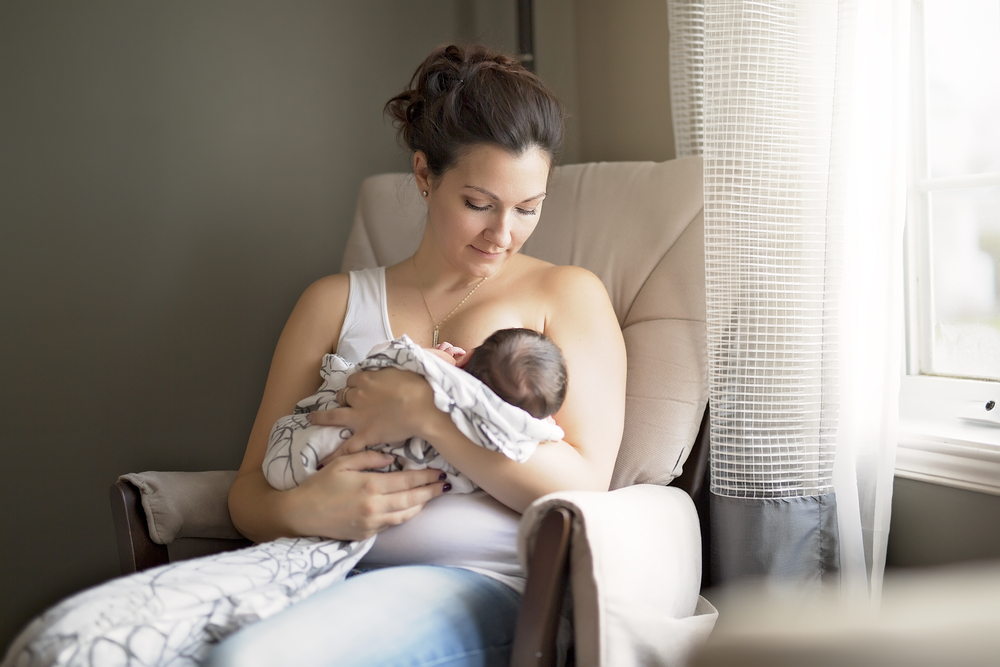

A mother's positive attitude, proper rest and frequent breastfeeding will help to quickly establish breast milk production.
The first thing is to calm down and wait for the milk. The mother must understand that the lactation crisis will definitely pass, and her child will not suffer from it. You need to wait for the milk in complete calm. It is a serious mistake to make an unreasonable mistake these days, which leads to a rapid suppression of milk production and the cessation of breastfeeding.
To make mommy confident in her victory, we can offer some useful tips that will never harm and will be useful in reducing milk production in any situation:
The main indicator of effective breastfeeding is sufficient weight gain of the child, his good health and active behavior. In conclusion, I would like to say that a woman who wants to breastfeed will breastfeed, and success depends only on her desire and aspiration.