
Lactostasis - stopping the movement through the ducts (stagnation) of breast milk, usually occurs in the first weeks of feeding a newborn. Primiparous women are more likely to suffer from this pathological condition. The disease usually occurs between the first three days and six weeks of breastfeeding. The consequences of lactostasis are the reproduction in an excellent nutrient medium of microbes that have entered through the cracks in the nipples into the gland, and the formation of purulent inflammation.
How to distinguish lactostasis from mastitis? The first is a non-inflammatory condition, with no signs of inflammation. When there is reddening of the skin of the gland, its swelling, severe pain and induration, an increase in local temperature in the area of the induration of a relatively healthy gland, deterioration in general well-being. Mastitis requires immediate medical attention.
The causes of lactostasis are primarily associated with the wrong way to feed a child. This is facilitated by nipple cracks that appeared in the first days of feeding. They are painful, disrupt the feeding technique and make pumping difficult.
With irregular attachment to the breast, impaired sucking, nerve impulses from the nipples and breast tissue carry incorrect information to the pituitary gland - a part of the brain. As a result, the production of prolactin in the pituitary gland decreases. This hormone regulates milk synthesis. Under its influence, oxytocin is also produced, which contracts the muscles of the uterus and stimulates the contraction of the milk ducts. As a result of a lack of prolactin and oxytocin, the lactation function of the ducts decreases, and acute milk stasis occurs.
Factors provoking the disease:
It consists in teaching a woman at childbirth preparation courses, the availability of an accessible daily telephone consultation at the request of the patient (“breastfeeding hotline”), and the proper organization of assistance to women who have given birth at the pediatric site.
A woman should also engage in self-education: read special literature, watch educational videos, listen to the advice of more experienced relatives and friends.
How to feed a child in order to prevent the development of lactostasis?
At the very beginning of the disease, a woman pays attention to the fact that milk began to stand out worse, in a thinner stream, intermittently. The behavior of the child also changes: he does not eat up, is capricious, quickly gets tired. Usually a day or two after this, the clinical picture of lactostasis unfolds.
Symptoms of lactostasis in a nursing mother: there is a strong engorgement of the gland, it thickens, becomes painful. More often the gland is affected on one side, less often on both. When pumping, patients are concerned about pain, a feeling of fullness, a weak outflow of milk. Sometimes there is pain in the armpits. It is associated with an increase in additional lobules of the mammary glands, located slightly away from the bulk of the secretory tissue.
Usually, a compacted area in the form of a “ball” or “cake” is palpated in the gland. The skin above it may turn slightly red, a venous pattern becomes visible on it. Such a zone can occur in different parts of the gland, changes its size and position.
Often, signs of lactostasis in a nursing mother include an increase in body temperature. In the people it is often called dairy. It does not exceed 38˚ and lasts no longer than a day. If the fever is higher or longer, accompanied by a deterioration in the woman's condition, it is possible that lactostasis has already been replaced by mastitis.
With lactostasis, the general condition of a woman does not suffer. She has no weakness, weakness, sleep and appetite are not disturbed. She is able to take care of her child.
To treat this condition, two main tasks must be performed: to free the mammary glands from stagnant milk and to establish its normal secretion.
It is necessary to establish the correct feeding regimen, sometimes completing it by decanting milk residues. You can use a breast pump for this. Suitable for both mechanical and automatic devices.
How often to express with lactostasis? This should be done no more than three times a day, emptying the corresponding mammary gland. At the end of each feeding, it is not necessary to express milk if the woman does not feel an urgent need for this. If the breast is full of milk, it is better to express it a little before feeding. You don't need to pump at night. Read our article below to learn how to drain lactostasis at the same time.
There is no need to limit drinking. Help reduce milk production sage, hop cones, leaf infusion walnut, garlic (up to 5 grams per day). But we should not forget that unusual plant foods can slightly change the taste of milk, and the baby will refuse to eat it.
Such a common remedy as a cabbage leaf can provide significant assistance to a woman with lactostasis. Firstly, a dense sheet heats up the tissue and improves its blood supply. Secondly, the active substances secreted by the plant have a decongestant, analgesic, vasodilating effect. Before use, it is recommended to cut the veins of the leaf, this will help the juice to be absorbed faster. It is best to apply the cabbage leaf after feeding the baby. It can be put directly into the bra cup after washing and drying. Such a sheet should be changed after two hours, there are no contraindications for its use.
Agents such as alcohol compress and camphor oil, as well as any other warming methods, are not recommended now, as they can cause mastitis or completely stop the production of milk.
Traumeel gel has practically no contraindications - a remedy based on herbal ingredients. It helps relieve swelling, pain and inflammation, improves the functioning of the milk ducts. With lactostasis, the medicine is applied to the skin of the gland twice a day, it is not harmful to the mother and child. In this case, a compress is not needed, the gel is simply applied to washed skin.
How to bring down the temperature that occurs during lactostasis without harming the baby? It is acceptable to use drugs such as Paracetamol or Nurofen. Do not take Aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Analgin.
Treatment of lactostasis at home is based on the use of folk remedies, tested by generations of Russian women, and on modern devices. It is based on three principles:
One of the necessary conditions for improving well-being is the elevated position of the gland. It is better for a woman to use special nursing bras that support her breasts and distribute pressure on wide straps. If the breast hangs freely, it creates excellent conditions for stagnation of milk.

You need to find several comfortable positions and alternate them.
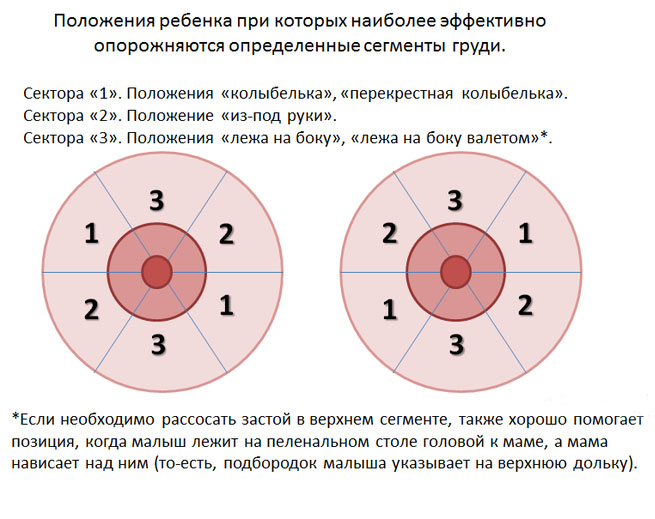
![]()
1. Baby on mom
2. Overhang

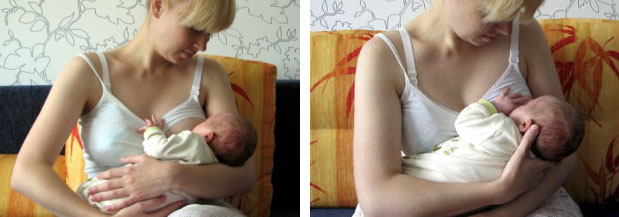
1. Lying on the arm
2. From under the arm
1. Cradle
2. Cross cradle
The so-called straining of lactostasis is used when simple methods do not help; carried out before feeding the child, at least every two hours:
What to do if home remedies for lactostasis do not help? Which doctor should I contact? Usually, a visiting nurse or a pediatrician who visits the mother and child and controls the process of breastfeeding helps to solve such problems. If home methods are ineffective, a doctor may prescribe physiotherapy or medications.
Physiotherapy methods are safe for women and children, painless and very helpful in restoring lactation. Ultrasound, electrophoresis of medicinal substances, ultra-high frequencies (UHF), darsonval are usually used. These procedures can begin even in the hospital if the problem with feeding arose immediately.
For treatment at home, you can purchase an apparatus for electrophoresis at the Medtekhnika store. Dimexide, Troxevasin and other blood circulation improvers can be used in it, but only after advice from a supervising doctor.
To improve the emptying of the gland, Oxytocin is prescribed intramuscularly before feeding or pumping. So that this drug does not cause painful uterine contractions, No-shpa is also injected intramuscularly half an hour before the injection.
To increase the volume of water, thereby reducing the amount of fluid in the body, diuretics are prescribed (Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide).
To reduce milk production, Dostinex or Parlodel are prescribed. They are prescribed literally for one or two days, with a longer intake, such drugs can completely suppress the formation of milk. Also, with severe lactostasis, which many authors consider as the initial form of mastitis, penicillin antibiotics are used that are safe for the child. They are prescribed to prevent the development of pyogenic microflora in the area of stagnation.
It would seem, how can milk stagnation occur in atrophied mammary glands in men? It turns out that such cases occur, although very rarely. They are usually associated with the release of milk under the action of the hormone prolactin. It is secreted in men as a result of a benign or malignant tumor of the pituitary gland, a gland in the brain. In addition, sometimes milk begins to be released with a deficiency of testosterone - the male sex hormone, lung tumors, hypothyroidism, excessive use of antidepressants, Verapamil and other drugs.
In these cases, a small amount of milk begins to stand out in men. Since their glands do not have a well-developed structure, milk can stagnate inside, accompanied by the same symptoms as in women: engorgement of the gland, the formation of a painful seal in it.
Treatment of lactostasis in men consists in the treatment of the underlying disease. They have fewer restrictions for drug termination of lactation with the help of hormonal drugs.
Laktostasis is a disease of the mammary gland during feeding and is characterized by blockage of one or more ducts. As a rule, mothers do not have difficulties in solving the problem of which doctor to contact with lactostasis, since even a pediatrician can help with this problem. The disease is common in those women who violate the basic principles of breastfeeding, which the gynecologist is obliged to inform about even during pregnancy.
The treatment of lactostasis is carried out by a doctor of mammological or gynecological profiles. You need to contact him as soon as the symptoms of the pathological process appear. These include:
With lactostasis, they go to the doctor, and do not try to get rid of the disease on their own because of the high risk of infection and the complication of pathology with mastitis. In addition, blockage of the ducts does not allow normal breastfeeding of the child, because of this, mixtures have to be made periodically. An unfavorable outcome of such interruptions in feeding will be the rejection of mother's milk.
The doctor diagnoses the disease using a clinical examination and additional research methods (laboratory and instrumental).
After the diagnosis is made, treatment is immediately prescribed, since breast milk is an excellent environment for pathogenic bacteria.
Women should consult a doctor as early as possible, during the first day of the development of the clinical picture of lactostasis.
To treat lactostasis, the doctor uses a special device that allows you to express milk. As a rule, for a mild degree of severity of the pathology, such measures are enough to solve the problem. However, the doctor must tell the woman about the causes of the disease and methods of its prevention.

A breastfeeding mother should follow the instructions of a specialist to avoid a relapse.:
Much more serious lactostasis is treated by a doctor if there are signs of inflammation and infection. At this stage of the progression of the disease, it is necessary to add antibacterial drugs to the therapy, and breast-feeding temporarily stops. Mastitis can also be complicated by an abscess or phlegmon, which will require surgical intervention. Therefore, at the first signs of lactostasis, a woman should consult a doctor.
Lactostasis - stagnation of milk that occurs due to blockage of the lactiferous duct, usually occurs in one mammary gland.
Milk accumulates in the breast due to the fact that it is poorly emptied, there is a milk plug in the duct.
First, edema of the glandular tissue appears, it manifests itself as a thickening of the chest area.
If the milk is in the clogged duct for a long time, the woman's body reacts to the proteins that make up its composition as foreign substances. A rejection reaction begins: the body temperature rises, soreness and redness of the compacted area occur.
This is not an infectious disease, and not a reaction of the body to hypothermia (“chose the chest”). This is a consequence of a violation of the outflow of milk.
Rarely, one of the following causes leads to lactostasis. In order for milk stasis to occur, several factors need to be “combined”.
Lactostasis develops gradually. If it is not eliminated in three to four days, it turns into non-infectious mastitis - inflammation of the breast tissue. Milk impregnates the tissues of the gland, it is a good breeding ground for bacteria that begin to multiply actively. Three days after the onset of non-infectious mastitis, infectious mastitis develops, which cannot be cured without antibiotics. Therefore, lactostasis must be dealt with in the first three to five days after the onset, so as not to treat its complications.
With lactostasis, the temperature rises in the axillary region, but when measured in the elbow and in the inguinal fold, it remains normal. If mastitis has developed, body temperature is elevated in all areas.
 Who to contact?
Who to contact?If independent attempts to cope with lactostasis are unsuccessful, you should contact a gynecologist or invite a breastfeeding consultant. At the first sign of mastitis, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Lactation
You can't stop breastfeeding! Some things need to be changed.
Non-drug methods for eliminating lactostasis
After feeding, cold compresses can be applied to the breast. They help the resorption of areas of compaction and relieve chest pain.
Cabbage leaf compress: a cabbage leaf is beaten a little with a hammer so that cabbage juice stands out better from it, and put in a bra. It is necessary to ensure that the leaf does not cover the nipple and the cabbage juice does not get inside the breast. Getting cabbage juice into milk will provoke abdominal pain in the baby.
Honey cake compress: mix honey with rye flour to make a stiff dough. Apply to the painful area.
Before the next feeding, the compress is removed, the breast is rinsed with warm water and given to the baby. After feeding, the compress is repeated.
Do not make compresses with vodka, camphor alcohol or ethyl alcohol. These substances disrupt the flow of milk from the breast. They suppress the secretion of the hormone oxytocin, which is responsible for pushing milk out of the mammary gland.
Physiotherapy methods
Ultrasound therapy is the most effective way to destroy lumps that have blocked the milk duct. But after its application, the formation of milk is significantly reduced. Therefore, you need to limit yourself to one or two procedures.
Do not affect the formation of milk and can eliminate lactostasis:
Medications
With an increase in temperature, severe pain, you can take a drug based on paracetamol or ibuprofen. They are compatible with breastfeeding.
A special solution is used for compresses on the compaction area, the solution is diluted with cold boiled water in a ratio of 1: 1, a cotton pad or gauze is moistened with it and applied to the painful area between feedings.
Antibiotics for lactostasis are not prescribed, they treat mastitis.
Mastitis is an infectious inflammation of the mammary glands, which most often develops in women after childbirth and is associated with breastfeeding.
Lactational (associated with breastfeeding) mastitis accounts for 95% of all inflammatory breast diseases in women. Mastitis not associated with breastfeeding is much less common and can occur even in men and newborns.
Most often, lactational mastitis develops 2–3 weeks after childbirth against the background of stagnation of milk in the mammary gland - lactostasis. Pathological lactostasis is often considered as the initial stage of mastitis. Stagnation of milk contributes to the development of an infection that enters the gland through microdamages, as well as through the milk ducts of the nipple from the newborn during feeding. If milk stagnates in the breast for a long time, bacteria begin to actively multiply in it, which leads to the development of inflammation.
Mastitis usually develops on the 3rd-4th day of lactostasis. With the timely elimination of milk stagnation, as a rule, it is possible to prevent mastitis.
The development of symptoms of mastitis occurs quickly, within a few hours. Without treatment, the condition gradually worsens, the symptoms worsen, the temperature becomes higher.
The initial stages of lactational mastitis can usually be managed with simple measures: massage, changes in feeding and pumping techniques, and physiotherapy. The later stages of the disease are very difficult, requiring antibiotics, weaning the baby from the breast and surgery. After a surgical operation, rough scars often remain, which spoil the appearance of the breast and force a woman to turn to plastic surgeons.
The insidiousness of lactational mastitis lies in the fact that its initial stages are very quickly and imperceptibly replaced by purulent ones. Therefore, at the first signs of breast disease, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid complications and long-term crippling treatment.
Mastitis usually occurs on one side, more often on the right. Manifestations of mastitis depend on the stage of the disease. Since the breast tissue is rich in blood vessels, milk ducts and adipose tissue, the infection spreads very quickly through the mammary gland without encountering natural barriers on its way, the stages follow each other.
Symptoms of the initial stage of mastitis - serous, differ little from lactostasis:
The serous stage of mastitis is replaced by an infiltrative stage - against the background of the persistence of symptoms in the gland, an area of compaction is determined, which is sharply painful when palpated. At this stage, mastitis can be stopped without surgery, the infiltrate can be forced to resolve.
Without treatment, within 3-4 days, the serous and infiltrative stages of mastitis turn into purulent. With suppuration of the tissues of the gland, the state of health deteriorates sharply: the temperature rises, pain intensifies, swelling of the mammary gland. Depending on the individual characteristics, an abscess can form in the tissues - an abscess or phlegmon limited to a capsule - a diffuse purulent inflammation of the gland without clear boundaries. In the latter case, mastitis is especially dangerous.
The immediate cause of mastitis is usually bacteria - Staphylococcus aureus or other microbes that are found on the surface of a person's skin. The infection enters the mammary gland through microdamages on the nipple or excretory ducts of the milk ducts. It is believed that the source of infection may be the newborn itself, which transmits microbes to the mother during feeding.
If the mammary glands are regularly emptied (during feeding and / or pumping), then the bacteria do not have time to multiply. When milk stagnates, microbes, multiplying, increase its viscosity, which aggravates lactostasis. Further development of the infection leads to purulent inflammation in the mammary gland.
Primary (physiological) lactostasis (milk stasis) is most common in women after the first birth, which is associated with a violation of the preparation of the mammary glands for feeding.
On the 3-4th day after childbirth, milk suddenly arrives, but the mammary glands are not yet ready to accommodate it. Excessive stretching of the milk ducts leads to their inflammation and swelling. Milk is excreted with great difficulty, so it is difficult for a newborn to suckle on his own, and he may refuse to breastfeed, which further aggravates the process.
If the necessary measures are not taken at this time, pathological lactostasis develops within a few hours. Its symptoms:
If milk is properly expressed, there is a rapid improvement in well-being, which never happens with already developed mastitis. In addition, you can note a significant difference in body temperature when measuring it in the right and left armpits: on the side where the chest is more tense and painful, the thermometer will rise higher. With the development of mastitis, this difference will no longer be. However, only a specialist can reliably distinguish the stage of pathological lactostasis from mastitis.
If you experience the symptoms described above after giving birth, seek help as soon as possible. At the maternity hospital, at any time of the day, you can go to the midwife on duty, who will help you “drain” your breasts and tell you how to do it yourself in the future. In addition, the midwife will teach you a massage technique that promotes the expansion of the milk ducts and the discharge of milk from the gland.
During your doctor's round, be sure to tell him about your breast problems. The doctor will examine the mammary glands, give you his recommendations and, possibly, prescribe additional treatment, for example, physiotherapy.
If you have milk stasis after you were discharged from the maternity hospital, seek medical help from a gynecologist or a breastfeeding specialist at a antenatal clinic.
It is necessary to fight lactostasis under the supervision of a doctor. Otherwise, you can miss the time and not notice the moment when lactostasis develops into mastitis.
Chronic mastitis is a rare disease that can develop in a woman at any age, usually after acute mastitis. The reason for the transition of the process into a chronic form is incorrect or incomplete treatment. With this disease, one or more purulent cavities are formed in the mammary gland. Sometimes cavities are opened through the skin with the formation of fistulas - passages through which pus periodically drains. Chronic mastitis requires surgical treatment.
Some women have a predisposition to stagnation of milk and the development of mastitis. Factors that increase the likelihood of these conditions include:
In these cases, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the mammary glands after childbirth, especially in the first 2–3 weeks, until lactation is finally established.
Non-lactating mastitis is more likely to develop in women aged 15–45 years:
The immediate cause of non-lactational mastitis is usually an infection. Bacteria can enter the mammary glands with blood flow from foci of chronic inflammation in the body, for example, with chronic tonsillitis, cystitis. In addition, non-lactational mastitis can be a consequence of trauma, including nipple piercing.
This disease can develop in children of both sexes and is associated with hormonal changes. After childbirth, a high level of maternal hormones is maintained in the baby's body for some time. When their level decreases (usually 4-10 days after birth), the baby may experience breast engorgement and even milk discharge from them. By itself, the physiological engorgement of the glands in newborns does not require treatment and resolves on its own.
But during this period, the baby's mammary glands are very vulnerable. If they become infected, mastitis may develop. The entry of bacteria is facilitated by non-observance of hygiene rules, rubbing of the mammary glands, attempts to squeeze milk out of them, diaper rash and skin diseases. The development of mastitis in newborns is accompanied by fever, anxiety and crying of the child, redness and enlargement of the mammary glands. These symptoms require urgent medical attention.
If you experience symptoms of milk stasis or mastitis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. This may be an obstetrician-gynecologist in a antenatal clinic, a polyclinic or a paid clinic. In addition, assistance with the development of lactostasis and mastitis can be provided in the maternity hospital where you gave birth. If it is not possible to get to a gynecologist, contact a surgeon. Diagnosis and treatment of mastitis is also within his competence.
The basis for the diagnosis of mastitis is an examination of the mammary gland. Probing it can be painful, but it is necessary for the doctor to determine the stage of the process and further treatment tactics. With lactostasis, during the examination, the doctor can “dissolve” the chest, which will immediately bring relief.
As an additional examination is assigned:
The sooner you seek medical help, the easier, shorter and more effective treatment will be. The onset of symptoms of mastitis should always be a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible. Remember that mastitis does not go away on its own, but on the contrary, it progresses rapidly and can deprive you of your breast within a few days. After all, nutritious breast milk is an ideal incubator for pyogenic microbes.
In no case do not delay time, relying on folk methods and advice from "experienced" friends. Cabbage leaf, honey cakes or urine therapy remained in the people's memory only because in the old days, when there were no antibiotics and other effective medicines, they were the only means of help.
A lot of experience has now been accumulated in the treatment of postpartum mastitis. For these purposes, both non-drug methods and drugs are used. Purulent stages of mastitis necessarily require surgical treatment. Moreover, the earlier the operation is performed, the better its therapeutic and aesthetic result.
According to the position of official Russian medicine, with the development of mastitis, it is necessary to stop breastfeeding. At the time of treatment, the child is weaned and transferred to artificial feeding. In exceptional cases, at the stage of serous mastitis, the doctor may allow healthy breastfeeding. However, the infiltrative and, moreover, purulent stages are clearly an indication for stopping feeding.
Weaning a baby from the breast is a very unpleasant measure for every mother, because there is nothing more useful for a baby than breast milk. However, with the development of mastitis, such a measure is a must. Continuing to breastfeed can harm your baby because:
Continuing breastfeeding for a woman with mastitis is also fraught with complications, since:
In addition, feeding with mastitis is an extremely painful process that will not bring joy to either the mother or the child.
Now on the Internet, and, sometimes, on breastfeeding courses, you can read or hear recommendations to breastfeed at all costs. Such advice is reassuring to women, and they continue to breastfeed through pain and suffering, to the detriment of themselves and the child.
In fact, the authors of such advice confuse the stage of lactostasis, when it is necessary to continue feeding, with mastitis. With lactostasis complete feeding and pumping milk the best medicine. During and after the emptying of the mammary gland, there really is relief. While with mastitis, the mere thought of feeding reflexively starts the process of milk production, which worsens the condition. Therefore, the issue of breastfeeding should be decided only by a doctor after a full diagnosis and determination of the stage of the disease.
Serous and infiltrative stages of mastitis are treated conservatively - without surgery. For treatment, drugs are used, as well as physiotherapy.
Milk is expressed every 3 hours. First, the diseased breast is decanted, and then the healthy one. Your doctor may give you antispasmodics (drugs that widen the milk ducts) in pill form or by injection before pumping.
Sometimes novocaine blockade of the mammary gland is done before pumping. To do this, using a long thin needle, an anesthetic solution (novocaine) is injected into the soft tissues behind the mammary gland - a substance that interrupts nerve impulses from the gland to the brain. After the blockade, the pain disappears for a while, the milk passages open, which greatly facilitates pumping. As a rule, antibiotics are added to the anesthetic solution to create their therapeutic concentration in breast milk.
Physiotherapy treatment is extremely effective for lactostasis and mastitis. At non-purulent stages of mastitis, ultrasound, microwaves, and UV radiation are used. Physiotherapy helps to reduce inflammation and pain in the gland, expand the milk ducts, improve the process of milk secretion, and prevent its stagnation in the gland.
Antibiotics are an essential component of mastitis treatment. For the best effect, antibacterial drugs are prescribed in the form of intramuscular or intravenous injections. During treatment, the doctor may change the antibiotic based on the results of a bacteriological analysis of milk and an antibiotic susceptibility test.
To speed up recovery and reduce the risk of purulent complications, it is necessary to temporarily reduce milk production. For this, with mastitis, special medications are prescribed.
At the stage of serous and infiltrative mastitis, milk production is somewhat reduced - inhibited. If no improvement is observed within 2-3 days from the start of complex treatment, and a high risk of complications is created, the doctor may advise you to completely stop - to suppress lactation. To do this, you will need to give written consent.
The decision to resume lactation will be made by the doctor after the end of treatment, depending on your well-being and the results of the tests. With purulent mastitis, it is always recommended to suppress lactation.
In addition to the main ones, additional drugs are used in the treatment of mastitis, which have a tonic, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effect.
With the development of purulent forms of mastitis, surgical treatment is always necessary. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Depending on the location and size of the abscess, the surgeon makes one or more incisions in the mammary gland. Pus and dead tissue are removed through these incisions. Then the wound is washed with an antiseptic solution and drains are installed - tubes through which the wound is washed, drugs are administered and the wound discharge is removed after the operation.
The operation is usually completed with sutures. If the postoperative period proceeds safely, the sutures are removed on the 8-9th day. After the operation, antibiotics and physiotherapy are prescribed to improve wound healing.
The basis for the prevention of mastitis is the timely fight against milk stagnation, the correct technique of feeding, pumping and caring for the mammary glands.
The physiological mechanisms of milk production, its accumulation in the breast and return during feeding are very complex. For their proper formation, a close relationship between mother and child is very important. Therefore, the initial measures for the prevention of mastitis are:
Every woman after childbirth should learn how to breastfeed properly. Improper feeding increases the risk of nipple cracks, milk stagnation (lactostasis) and, in the future, mastitis.
A woman should be taught the technique of proper feeding by the attending obstetrician-gynecologist or midwife. For all breastfeeding questions, you can contact the staff of the maternity hospital.
Basic rules for breastfeeding:
1. Before feeding, you need to take a shower or wash yourself to the waist with warm water and baby soap, you can wash your breasts only with water so as not to dry the skin of the nipples.
2. You should take a comfortable position: sitting or lying down, so that there is no feeling of fatigue in the muscles and there is no need to change body position, interrupting feeding.
3. The child must be securely held by your hand near you, after making sure that even if you fall asleep during feeding, the baby will not fall. To do this, you can put a pillow under your arm or fence off the edge of the bed with a roller from a blanket.
4. During feeding, the entire body of the child should be turned towards the mother, the head and back should be in the same line, the baby's mouth should be opposite the nipple. The child should be able to move his head freely to get comfortable.
5. The most important point is the correct grasp of the breast during feeding. The baby should take the breast with a wide open mouth, not only the nipple, but also most of areola- areola. The lower lip of the baby during sucking should be turned outward.
6. If the baby sucks rhythmically and deeply, does not worry, does not puff out his cheeks and does not choke, and you do not feel pain during sucking, then everything is correct.
7. If it is necessary to interrupt feeding, do not pull the breast out of the baby's mouth, this can injure the nipple. To painlessly remove the breast, gently press your finger on the chest near the baby's lips, then the nipple can be easily released.
8. After feeding, the remaining milk must be expressed. If there are phenomena of lactostasis, then the baby is first of all applied to the diseased breast.
With the phenomena of lactostasis, manual pumping is more effective, although this is a very laborious and sometimes painful process.
The skin of the mammary glands, especially the oklososkovy circle, is very vulnerable, through damage to the skin, an infection can penetrate into the mammary gland. Therefore, you must adhere to the following rules:
You can get additional advice on breastfeeding and mastitis prevention at the antenatal clinic or at the pediatric clinic for children.
lactostasis is a violation of the outflow of milk from the mammary gland during breastfeeding. Most often this happens with flushes, or when milk first arrives, or when you are already at home, often at 3 weeks after birth, but a similar problem can occur at any stage of breastfeeding. Very often, women first learn what it is when weaning a child from the breast.
Violation of the outflow of milk during breastfeeding is especially common in the first days after childbirth, however, as a rule, a woman is still in the hospital, and doctors help her cope with it. The midwife shows how to express properly, if necessary, physiotherapy and medications are prescribed to help the milk flow freely.
The reasons for the appearance of such disorders after childbirth and during the rush of milk is that the fluid is more than the baby needs, and because of this, part of it stagnates. However, in a nursing mother, it can also occur for other reasons.
Improper underwear for nursing, squeezing the breast, improper breastfeeding technique can cause a violation of the outflow of milk from any one lobe of the mammary gland, and then this complication is also possible. It is impossible to pinch the nipple area with your fingers (scissors) during breastfeeding, as you violate the outflow of milk.
Frequent violations torment women with mastopathy. The fact is that with mastopathy, fibrous tissue grows in the mammary glands, which has a very dense structure and can compress the ducts of the mammary glands, disrupting the outflow of milk. In a nursing mother, this develops due to the formation of the so-called milk plug, when the mammary duct becomes clogged and milk cannot flow freely, and this is the main cause of the disease.
Whatever the causes of the violations, it is necessary to take it very seriously, since mastitis, inflammation of the mammary gland, can begin with it.
Symptoms:
The appearance of a lump in the chest
- an increase in body temperature (at a temperature above 38 - immediately consult a doctor, is it mastitis?)
- a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the chest, later burning, and finally pain.
- in an advanced case, the skin turns red, and then it can be difficult even for a doctor to determine what it is, lactostasis or mastitis without ultrasound and tests.
Why does a lump appear in the chest?
Stagnation does not develop immediately in the entire mammary gland, milk is retained in individual lobes. It is related to the structure mammary gland, it consists of many lobes, each of which has a duct that opens in the nipple area. And milk can flow freely from all but one, this milk-filled lobule can be felt in the chest. Most often, the lobes of the mammary gland located in its lower outer part suffer. After this, the seal disappears, however, if the woman was not treated and at the same time avoided mastitis, the breast tissue can be so seriously affected that instead of a normal lobule, a cicatricial degenerative seal remains.
Another very characteristic symptom is fever. If you suspect. that not everything is in order with the mammary glands, a high temperature can be both due to the fact that milk that is not able to flow destroys and causes inflammation of the breast lobe, and due to the fact that mastitis has begun to develop, that is, microbes have joined the inflammation, and now everything can end badly without serious timely treatment, you will have to do an operation.
Important: during lactation, do not measure the temperature in the axillary region, it is elevated here even in normal conditions with a rush of milk. Always measure it at the elbow. Unlike a high temperature with a cold, you may not feel this rise in temperature, the condition remains quite good.
It is worth knowing how to distinguish lactostasis from mastitis, since in the second case it is already a purulent-inflammatory disease that requires antibiotic treatment, and with late treatment of surgical treatment, since an abscess forms in the chest.
Mastitis is very dangerous and develops quickly, usually it takes 2-3 days until the scalpel is indispensable. It can develop both as a result of stagnation, and independently. His symptoms are the same - chest tightness and fever. But if in the first case it does not appear immediately, and at first it is only with pressure on the seal, with mastitis, the chest hurts very much, and the skin over the seal turns red and becomes hot very quickly. If you can't deal with fluid retention in your breasts within two days, the risk of mastitis becomes very high. Knowing what it threatens you do not spend precious hours on self-treatment, and immediately consult a doctor.
It often happens that a nursing woman finds a lump in her chest at the most inopportune time, and cannot immediately see a doctor, but in most cases you can get rid of this ailment on your own by starting pumping and breast massage in time.
Pumping is a necessity, and statements that milk will burn out anyway are not true. Yes, the more milk is expressed, the more it is formed, but the task is not to express all the milk, but to release the stagnant lobule of the mammary gland.
Even if you have a suspicion of outflow disorders, feeding must be continued, your child is your best doctor in such a situation, and during feeding, you need to use postures that help release the mammary gland from milk in those areas where it has accumulated, for example, arm feeding is often effective. The fact is that when sucking, the baby better releases from milk those lobes of the mammary gland that bear the pressure of his lower jaw. In women who use different positions constantly while breastfeeding, stagnation occurs less often, it is worth mastering all possible feeding techniques. Before feeding, it is advisable to express the diseased breast and start feeding the baby from it, so he is more likely to be able to cope with the stagnation of milk.
How to express properly?
Grasp the mammary gland with a seal with the same hand so that it lies in your palm, thumb on top, the rest support and lift it. In this position, the excretory ducts of the mammary gland are opened in those areas where they usually suffer most often.
How to strain lactostasis?
Your fingers, index and thumb, do not lie on the nipple itself, but on areola. You will feel a bumpy surface under the nipple - these are the ducts of the mammary glands. There is no need to pull on the nipple itself, pump it, massaging these "tuberosity" under the nipple. Milk will flow painlessly, the nipple will not be injured. At the same time, with the other free hand, the area of densification is massaged from the outside to the center of the mammary gland, freeing it from milk. Usually the milk squirts out in strong streams if done efficiently enough. At the end of the article is a video on how to do it right.
Facilitates pumping by taking a tablet no-shpa 20-30 minutes before feeding, a heating pad applied to the breast and pumping after you feed the baby. You can do this under a warm shower, it also helps (from the second day from the onset of the disease, it is no longer possible to warm the chest).
It is far from always possible for a woman to immediately learn how to express herself correctly, any pregnant woman among the numerous dowry should not forget to buy a good breast pump. Today, their choice is very rich, you should not save on this.
In the pharmacy you can see breast pumps in a variety of price categories. From tiny old-style pear-shaped ones that are not at all effective and traumatic to the mammary gland, to expensive, high-quality creations from AVENT and others, with a soft silicone pad that imitate the sucking movements of a child.
If within a day or two the struggle goes on with varying success, milk accumulates again and again, the body temperature rises again, it is not possible to defeat the disease on your own, decide how to treat it further with your doctor.
One of the questions that puzzles a breastfeeding mom who has had a churn is which doctor to go to?
This problem is dealt with not only by gynecologists and mammologists; first of all, an observing pediatrician can help. You can choose to go to a gynecologist, mammologist or pediatrician, depending on whose consultation is available faster. If you suspect mastitis, you will need to see a surgeon.
Among the methods of treatment that are prescribed by a doctor, there are both drugs and physiotherapy. Let's go over all the options. As a rule, complex therapy is recommended, but you need to understand that the main task of treatment is to free the breast from milk stagnation, and all the methods of treatment used are nothing more than helping mom in this sometimes such a difficult process.
Ointments and compresses for lactostasis
The task of all ointments and compresses is to reduce the swelling of the mammary gland and relax the spasmodic milk ducts so that the milk flows better. The ointment should also reduce inflammation and not be toxic, since the components of any ointment can be absorbed through the skin, and the baby sucks on the breast and everything gets to him. In addition, ointments with a strong odor can cause breast rejection.
So, what is most often used:
Traumeel
Traumeel C, the most commonly used ointment. This is a homeopathic safe preparation that can relieve swelling and redness and is not dangerous for the child. Traumeel does not have a strong odor, you can lubricate the breast every time after decanting, however, before giving the breast to the child, you need to wash it with warm water so that not a drop of ointment gets into the baby.
Vishnevsky ointment
Vishnevsky's ointment is definitely not worth using. The action of the ointment consists in a sharp rush of blood to the place that is smeared with it, which can lead to a rapid transition to the "mastitis" stage. The composition of the ointment contains birch tar and other substances that have a sharp specific odor. Even by washing off the ointment with soap, you will not get rid of the smell, and so you will lose your main ally, the child with a high degree of probability may refuse to breastfeed.
Malavit
Ointment Malavit has become an amazing and indispensable assistant for all occasions in many families. It can also be used, it is safe, most importantly, do not forget to wash it off the chest before feeding. Use it between feedings, lubricating the sore spot after expressing milk, it will help relieve swelling and inflammation.
Camphor oil
Camphor oil is not very suitable for the treatment of this problem because of the pungent odor, the baby can give up the breast, it is better not to risk it, although it could help by itself. But our task, first of all, is to strain the chest, and no one knows how to do this better than children.
Dimexide
Compresses with dimexidum should not be done categorically. This substance is prohibited for use in pediatric practice due to its proven toxicity, while dimexide is easily absorbed through the skin, which means that the child will receive it with milk.
Magnesia
Magnesia in ampoules of 10 ml is sold in a pharmacy. It is safe for you and your baby and is odorless. You can safely use it for compresses, as it relieves tissue swelling well. It is enough to simply rinse the breast before feeding (magnesia when taken orally weakens, and the baby may develop diarrhea if he tastes it). Put the magnesia-soaked gauze in your bra between feedings, expressing your breasts.
Oxytocin
Oxytocin injections are widely used in the maternity hospital. It not only improves the outflow of milk, but also helps to reduce the uterus of the woman who has given birth, a double benefit, you should not refuse an injection. You won’t be able to use it at home, and the farther from childbirth, the less effective this remedy is. Oxytocin is safe for the baby.
Pills
If a nursing woman has congestion in the chest, the tablets are not used, except when it is necessary to completely stop lactation. In such a situation, a better remedy than bromocriptine has not yet been invented. Lactation stops in a couple of days when taking pills according to the scheme. It is clear that this method of treatment is absolutely not suitable for women who intend to continue breastfeeding.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics can only be prescribed by a doctor if there is a threat of developing acute purulent mastitis. The drug of choice is erythromycin, as it can continue breastfeeding, and at the same time, it is effective against most microbes that cause mastitis.
How to bring down the temperature with lactostasis?
The high temperature is due to the stagnation of milk, and it immediately decreases as soon as the breast is freed from it. Reception of paracetamol is possible, but ineffective. To bring down the temperature, it is necessary to express the chest.
Ultrasound treatment is the most common method. Usually 3-4 procedures are prescribed, the mammary gland is massaged over the seal with the sensor of the ultrasonic apparatus for physiotherapy, after which the milk must be immediately expressed. It usually comes off very easily. It is not recommended to feed the child with this milk, that is, before treatment, your baby must eat, and after that, physiotherapy is carried out, after which you will have to empty the breast with your hands into some container right in the treatment room.
If you have a Vitafon device at home, you can be treated with it. You can also do no more than three procedures, 1 time per day, and do not feed the baby with milk.
Why such a limit on the number of procedures?
There is little milk precisely in those cases when physiotherapy was used, and the more sessions there were, the easier it is to lose breastfeeding later.
Among the most popular remedies in folk medicine was the cabbage leaf. It was used as follows: a leaf of white cabbage, clean, taken from the center of the head, beaten with a rolling pin until it gives juice, and applied to the chest.
Another well-known remedy is honey cake. You can use a combination of cabbage leaf and honey cake, lubricating the beaten cabbage leaf with honey and applying to the chest. Such a compress relieved inflammation and swelling, now it’s not at all necessary to mess with cabbage, there are excellent homeopathic remedies that cope much better with this.
Important: You need to limit your drinking! Try to avoid hypothermia. When feeding, support the breast from below, after feeding, apply cold to the breast. Feed on demand, don't sleep on your stomach, and be sure to wake up for night feeds even if your baby isn't crying.
In order not to wonder how to cope with this problem in the maternity hospital in the first days after childbirth, be sure to buy yourself a good quality breast pump in advance. Vacuum is enough, as long as it is comfortable and does not injure the nipples.