
Vomiting in infants, if it is repeated and plentiful, should not be left without the attention of parents and medical assistance. In combination with diarrhea and high fever, this symptom can lead to severe dehydration and weight loss. Also, vomiting can signal serious pathologies and disorders.
There are a huge number of diseases that are accompanied by a gag reflex. It is designed by nature that the body reacts to intoxication in the form of vomiting and diarrhea. Vomiting in case of poisoning, acute intestinal infections leads to a speedy recovery and relief of the baby's condition. Therefore, one should not rush to suppress it with antiemetic drugs. But if this symptom is not accompanied by fever and diarrhea, the cause may be in the inflammatory processes of the digestive organs (gastritis, colitis, pancreatitis, etc.). Perhaps there are congenital pathologies of the digestive organs, neurological abnormalities.
Causes of vomiting in infants can be more than serious. Thankfully they are rare.
It is extremely rare in infants. This is due to the type of nutrition and the anatomical features of the appendix. In addition to the gag reflex, the baby may have diarrhea, bloating, lethargy, anxiety, paroxysmal, severe pain, during which he pulls his legs to his stomach, severe crying. On palpation at the location of the appendicitis, the baby reacts painfully. It is extremely difficult to diagnose acute appendicitis in infants. An abdominal x-ray should be taken. In newborns, death occurs in 80% of cases, in infants up to a year - in 10%.

If a small researcher swallows a large object, he may stop in some part of the esophagus. The muscles of the esophagus contract reflexively, a gag reflex occurs. Vomit may contain streaks of blood and mucus. It is good if the baby manages to push the object back during the gag reflex. If the child behaves restlessly, he has breathing problems, there is a strong salivation, you should immediately call an emergency ambulance.
It can be congenital or acquired after severe infectious diseases with intestinal damage. It happens full and partial. Vomiting in a newborn with suspected intestinal obstruction occurs in the first days of life. The baby has a strongly swollen belly, in the vomit there are impurities of bile and meconium primordial feces. These are dangerous symptoms. The child needs examination and immediate treatment. Such a baby is stopped being fed orally, the body is supported with the help of droppers.
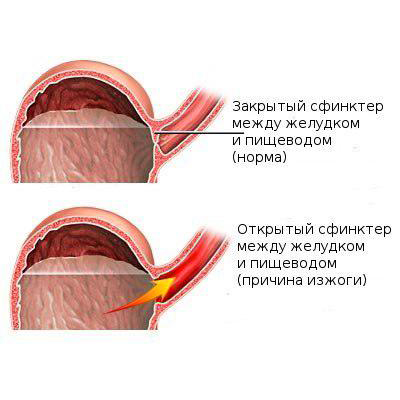
 The opening between the stomach and esophagus is called the cardiac sphincter. Its congenital expansion leads to the fact that food from the stomach constantly flows into the esophagus. The gag reflex can occur suddenly when the baby lies on his back or on his side, rolls over onto his stomach. It is recommended to eat in an upright position, you need to give a mixture or breastfeed only in fractional portions.
The opening between the stomach and esophagus is called the cardiac sphincter. Its congenital expansion leads to the fact that food from the stomach constantly flows into the esophagus. The gag reflex can occur suddenly when the baby lies on his back or on his side, rolls over onto his stomach. It is recommended to eat in an upright position, you need to give a mixture or breastfeed only in fractional portions.
Usually, with age, the work of the cardiac sphincter normalizes. However, with persistent vomiting and poor weight gain, you should see a doctor. You may need to consult a surgeon. A pediatrician with such a diagnosis may recommend switching to antireflux mixtures - baby food with a viscous consistency. This is a temporary replacement. After feeding with a thick mixture, as soon as the baby feels better, you can switch to the usual food. Also, the doctor may prescribe medications to reduce the tone of the muscles of the digestive system.
Neurological diseases can be laid even during intrauterine development as a result of oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia), during childbirth (asphyxia), after birth. In infants, against the background of a constant gag reflex, there may be increased excitability, chin tremor, strabismus, convulsions, lethargy. Often, neurological problems occur in premature and low birth weight babies. Such babies are observed for a long time by a neurologist, treated in a hospital.
 The narrowing of the passage between the stomach and duodenum is called pyloric stenosis. Refers to congenital pathologies. The inability of the contents of the stomach to move further along the intestines leads to profuse vomiting with a fountain. The disease makes itself felt in the first month of life. Vomiting is frequent and profuse, has a curdled consistency, the child behaves restlessly, is always hungry, quickly loses fluid and weight. With an accurate diagnosis, treatment involves surgery.
The narrowing of the passage between the stomach and duodenum is called pyloric stenosis. Refers to congenital pathologies. The inability of the contents of the stomach to move further along the intestines leads to profuse vomiting with a fountain. The disease makes itself felt in the first month of life. Vomiting is frequent and profuse, has a curdled consistency, the child behaves restlessly, is always hungry, quickly loses fluid and weight. With an accurate diagnosis, treatment involves surgery.
Pylorospasm is a narrowing of the pylorus muscles (the opening between the stomach and the duodenum). This deviation is referred to as functional disorders, because it is typical for many babies up to 4 months old. After birth, the baby has an increased level of the hormone gastrin, which leads to the tone of the pylorus muscles. Constant muscle contraction causes a rapid gag reflex. Vomiting with pylorospasm is not as profuse and frequent as with pyloric stenosis. Gradually, the pylorus muscles relax, and the gag reflex decreases. With obsessive vomiting in infants after feeding, the doctor will recommend switching to antireflux mixtures.
It occurs as a result of head injuries, the result of falls from a height, which, alas, happen to young children. Brain tumors, meningitis, encephalitis and other dangerous infections can also be the cause. The gag reflex does not necessarily follow after eating, it can appear suddenly. Accompanied by drowsiness, weak pulse, pale skin.

Most often there is a characteristic "duet" of symptoms - vomiting and diarrhea. There is also a "trio" - temperature, vomiting and diarrhea. What disease are they talking about?

Sometimes regurgitation after feeding can be mistaken for vomiting and vice versa.
Regurgitation is a natural involuntary throwing of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus, and then into the pharynx and oral cavity. Most often occurs 10-15 minutes after feeding, sometimes later - after 30-40 minutes. Regurgitation in most cases is a physiological process. Less commonly, it indicates pathologies and disorders. Usually children spit up when overeating, swallowing air during feeding, active movements after eating. This is due to the immaturity of the sphincters of the digestive system. General well-being during regurgitation is not disturbed. The baby may burp and not notice, not react to it in any way.
Vomiting is a reflex discharge into the esophagus, and then into the pharynx and oral cavity of the contents of the stomach. This process involves the abdominal muscles and the diaphragm. The gag reflex is regulated by the vomiting center, which is located in the brain. Before vomiting, a number of signs appear: nausea, pallor, profuse salivation, rapid breathing. During vomiting, the baby behaves uneasily. Usually the volume of vomit is greater than the volume of food taken, because gastric juice is added to undigested food.
How to distinguish vomiting from regurgitation in infants? According to the characteristic signs of vomiting:

If vomiting is accompanied by such signs and circumstances:
What should be done before the doctor arrives? Do not panic, be close to the baby all the time, keep him in an upright position and try to move him less, temporarily do not feed, in no case use antiemetic drugs, do not try to wash the stomach. You also need to wash the baby after bouts of vomiting so that the vomit does not irritate the delicate skin, rinse the baby's mouth.
The gag reflex is a defense mechanism of the body. In acute intestinal infections and poisoning, it helps the body get rid of harmful toxins. However, with persistent and frequent vomiting, complications can occur.
If the baby has profuse vomiting and rapid weight loss, it is necessary to solder it with glucose-salt solutions. You can drink from a teaspoon or from a syringe, pouring small portions over the cheek. The most famous trade names for drugs are Regidron, Hydrovit, Trihydron, Reosolan, Oralit and others. Rehydration solutions are sold in pharmacies without a prescription in powder form, it must be diluted in chilled boiled water according to the instructions.
Vomiting baby- always a reason to go to the pediatrician. It is better to play it safe, examine the baby in order to exclude pathologies and acute intestinal infections. All this must be done when vomiting is repeated and profuse, or accompanied by fever and diarrhea. If it was a single one, did not entail any other signs, and the baby feels well, the doctor will assess his condition as safe.
Many parents have had to deal with a situation where their baby pushes, strains, and subsequently vomits. After that, the baby may be lethargic, lose appetite and look unhealthy. In fact, vomiting in infants can be both a harmless phenomenon and a sign of a disease. This is especially true in cases where vomiting accompanies diarrhea and high fever.
The intervention of a specialist will also be needed when the vomit is interspersed with yellow or green contents, and the process itself occurs quite intensively and often. It is worth remembering that any, even a single vomiting in a child can lead to serious dehydration. In any case, it will not be superfluous to show the baby to a specialist.
First of all, the mother of an infant must be able to distinguish between normal regurgitation, which is quite common after feedings, and vomiting when it is a symptom of a serious problem.
The most common causes of vomiting in infants:
If vomiting has a single character and after it the baby feels fine, then such a case can be classified as reflex. In this way, the child tries to get rid of third-party substances that are not familiar to his receptor and taste preferences. This is a fairly common phenomenon in infants and can be, for example, when trying to give a child some kind of medicine with an unpleasant bitter taste, etc.
Vomiting is especially dangerous if it occurs in a fountain, repeats 3 or more times a day, and also at the same time the baby refuses food, looks tired. In addition, vomiting should cause concern, which is accompanied by fever or diarrhea. In such cases, self-medication can be dangerous to the health of the child. It is better to consult with a pediatrician, and in especially severe cases, call an ambulance immediately.
 Quite often, vomiting in infants is classified as normal regurgitation. This phenomenon is common among babies due to the underdeveloped digestive system, which does not cope well with the digestion of food, especially in large volumes. Regurgitation after feeding, sometimes even a fountain, is the most harmless vomiting. At the same time, the gastrointestinal tract is freed from excess food that it cannot cope with. At the same time, the process of vomiting itself occurs naturally, the baby does not strain, and the remnants of food spontaneously pour out.
Quite often, vomiting in infants is classified as normal regurgitation. This phenomenon is common among babies due to the underdeveloped digestive system, which does not cope well with the digestion of food, especially in large volumes. Regurgitation after feeding, sometimes even a fountain, is the most harmless vomiting. At the same time, the gastrointestinal tract is freed from excess food that it cannot cope with. At the same time, the process of vomiting itself occurs naturally, the baby does not strain, and the remnants of food spontaneously pour out.
To avoid regurgitation after feeding, mothers need to do simple manipulations, for example, hold the baby in an upright position for some time after feeding (how to do it right?), try to ensure that he is as calm as possible, do not bathe the baby immediately after feeding and limit his activity.
Other common causes of vomiting after or during a feed may include:
 Physiological vomiting in infants is the norm, if diarrhea is not present and body temperature does not rise. This phenomenon is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the gastrointestinal tract of the child. With normal regurgitation, the volume of the contents poured out should not exceed 5 ml of the food taken. However, many parents do not understand what to do if the baby spits up too much, like a fountain. In this case, this may be a signal of possible congenital pathologies or diseases. Only a specialist can help to make the correct diagnosis, therefore it is recommended to show the child to the pediatrician.
Physiological vomiting in infants is the norm, if diarrhea is not present and body temperature does not rise. This phenomenon is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the gastrointestinal tract of the child. With normal regurgitation, the volume of the contents poured out should not exceed 5 ml of the food taken. However, many parents do not understand what to do if the baby spits up too much, like a fountain. In this case, this may be a signal of possible congenital pathologies or diseases. Only a specialist can help to make the correct diagnosis, therefore it is recommended to show the child to the pediatrician.
The most common cause of spitting up a fountain can be improper attachment to the breast, when in the process of feeding the baby greedily captures a lot of air that fills his stomach. As a result of such a meal, the baby may experience not only vomiting, but also colic, bloating. This condition is not considered dangerous for the health of the baby, however, a specialist consultation will not hurt, especially if regurgitation is systematic.
Read: About proper breastfeeding.
Vomiting can be a symptom of a serious health problem in the baby, especially if there is diarrhea or fever. Various infectious diseases can be transmitted to the child through breastfeeding from the mother.
It is very important for a nursing mother to observe personal hygiene. Before each feeding it is necessary to wash the breast with warm boiled water. A similar procedure should be carried out after feeding.
With HB, malnutrition of a nursing mother can provoke vomiting in a nursing baby. Some products that are classified as “forbidden during breastfeeding” can provoke not only allergic reactions, but also inflammatory diseases of the digestive system.
If the child has diarrhea and vomiting, then these may be symptoms of food poisoning. If poor-quality or spoiled food has entered the child's stomach, parents should urgently take all measures so that it is absorbed into the blood in minimal quantities. Another dangerous moment in case of poisoning, accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting, is dehydration of the crumbs. In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance or consult a doctor.
Before the arrival of the ambulance, the baby must be given plenty of water, a diluted bag of Smecta or a diluted tablet of activated charcoal.
Intestinal infections and poisoning in infants are treated only in a hospital under the supervision of a specialist. Self-treatment is unacceptable, as it can become a serious threat to the health and life of the baby.
Parents know that in the first years of life, the baby frequent vomiting. This phenomenon looks like the release of previously eaten food through the mouth. Sometimes some parents think that vomiting and spitting up are the same thing. However, this is misleading. When spitting up, food is excreted through the mouth due to overeating. When a newborn vomits, it is due to spasms in the lower stomach. But there are cases when vomiting also arose as a result of overeating.
 If the baby constantly releases food masses from the stomach through the mouth, then this is a reason to be wary. It is possible that this is due to the not fully developed gastrointestinal tract, which is not yet able to effectively perform its basic functions. You should not worry about this, because it takes quite a lot of time for the baby and his body to adapt to this world.
If the baby constantly releases food masses from the stomach through the mouth, then this is a reason to be wary. It is possible that this is due to the not fully developed gastrointestinal tract, which is not yet able to effectively perform its basic functions. You should not worry about this, because it takes quite a lot of time for the baby and his body to adapt to this world.
But children grow up quite quickly, and therefore very soon their body will learn Right process food. If, after a few weeks, and even more so months, vomiting in the baby does not disappear, and the frequency of its manifestation remains at the same level, then this is a reason to consult a doctor for advice.
If you are increasingly experiencing gastric emptying in your child, keep in mind that it may indicate the presence of a serious illness. Due to frequent vomiting in the baby, dehydration. At the same time, there is a threat to his life if the vomit can enter the respiratory tract. Therefore, young parents need to be especially attentive to how the child behaves in the first years of his life.
 The first thing I would like to say is that there are several types of vomiting that can occur in the first years of life in infants:
The first thing I would like to say is that there are several types of vomiting that can occur in the first years of life in infants:
Vomiting in the baby, which manifests itself in the form of an independent eruption and spasms of the stomach, as a result of which not only food, but also other formations come out - slime, blood, indicates that the child has a certain disease. This pathology can occur in a little man for a variety of reasons. Experts currently distinguish several main ones:
However, these are not all the reasons why a small child may experience symptoms vomiting. Observing the condition of the baby, you need to pay attention to the composition of the vomit. If parents saw in them not only milk, but also foreign formations in the form of bile, blood and mucus, then this is a signal that you should immediately consult a doctor for an examination. It is likely that a serious disease develops in the child's body, which can only be detected by an experienced doctor.
 In the event that vomiting occurs in an infant infrequently without temperature and at the same time its composition is quite normal, this phenomenon can only be explained by a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
In the event that vomiting occurs in an infant infrequently without temperature and at the same time its composition is quite normal, this phenomenon can only be explained by a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the involuntary release of food through the mouth is very rare, then most likely the cause of the pathology is infection of the genital organs. If appendicitis is the cause of the ailment, then it can be detected not only by vomiting, but also by sharp pains in the abdomen, due to which the baby will make piercing cries.
If the cause of vomiting is a violation of the gastrointestinal tract, then a similar symptom of the disease is considered to be secondary. Be that as it may, vomiting, which makes itself felt not only by the release of liquid masses, but also by an increase in temperature, is sufficient reason to immediately undergo an examination in a hospital or call an ambulance at home.
Young parents can very easily confuse vomiting with regurgitation, so you should elaborate on this. You should not worry about this phenomenon, since this often occurs in an infant due to overeating or air entering the stomach, which does not pose a serious threat to the health of the baby. When a child has regurgitation, only the remnants of food can be found when leaving the mouth. There is nothing to worry about, so there is no reason to think about the presence of a serious pathology.
 Young mothers caring for baby for a long time, they gradually get used to the fact that after the next feeding the baby begins to spit up. But in some cases, an atypical reaction of the child's body may occur in the form of an active release of food through the mouth. The first thought a mother might have is child poisoned by milk. However, it is not. All this is a consequence of aerophagia, that is, when a child swallows air while sucking at the breast. Vomiting in the clinical picture resembles regurgitation, but here the process of food excretion is more active, which can confuse young parents.
Young mothers caring for baby for a long time, they gradually get used to the fact that after the next feeding the baby begins to spit up. But in some cases, an atypical reaction of the child's body may occur in the form of an active release of food through the mouth. The first thought a mother might have is child poisoned by milk. However, it is not. All this is a consequence of aerophagia, that is, when a child swallows air while sucking at the breast. Vomiting in the clinical picture resembles regurgitation, but here the process of food excretion is more active, which can confuse young parents.
In fact, this is not a reason to panic. Just when food comes out of the stomach in this way through the mouth, it indicates that the baby was not properly attached to the mother's breast. In such a situation, you need to do the following - remove the remaining air, and the drunk milk will come out with them. Most babies often burp after vomiting like this.
You can prevent the recurrence of vomiting after feeding if you are careful while eating the baby. To do this, it must be kept in the correct position. When the baby finishes eating, it should be held for a while with a column - this will help remove air from the stomach that has got along with milk. After a while, you can hear the characteristic sound of belching, but food will not come out of the baby's mouth. Based on this, we can say that the feeding procedure was carried out correctly.
![]() Vomiting in infants can be caused not only by the penetration of air into the stomach along with milk, but also by the wrong daily routine. If, after eating, the child immediately begins to play active games, or the parents begin to rock or shake him, then all this will eventually end with the appearance of vomiting.
Vomiting in infants can be caused not only by the penetration of air into the stomach along with milk, but also by the wrong daily routine. If, after eating, the child immediately begins to play active games, or the parents begin to rock or shake him, then all this will eventually end with the appearance of vomiting.
Just put yourself in the place of a child: even an adult can experience discomfort in the abdomen if, after a meal, they start shaking it or doing other similar actions with it.
As a result, a favorable situation will arise for the reverse exit of food. This can happen with young children as well. Moreover, this happens much more often due to the fact that their body is not yet adapted to the new conditions of life. If the baby begins to sway immediately after feeding, then this will necessarily negatively affect the work of the digestive system. To prevent this from happening to your child, make it a rule not to disturb him for half an hour after eating.
 In addition to the negative consequences described above, after eating, the child may also sometimes experience vomiting with a fountain. This phenomenon can be explained by various reasons - overfeeding, the presence of serious diseases.
In addition to the negative consequences described above, after eating, the child may also sometimes experience vomiting with a fountain. This phenomenon can be explained by various reasons - overfeeding, the presence of serious diseases.
If the baby is fed only with natural milk, then it will be very difficult for his parents to control the amount of food he eats. A baby can suckle for a very long time, which can eventually end with an overflow of the stomach. The physiology of young children is such that their stomach has a very small volume, and its walls do not yet have the ability to stretch. If he eats more than his stomach can hold food, then the internal pressure in it will rise and then spread to the valve of the stomach and esophagus.
Due to the pressure, the walls of the stomach will begin to contract, and as a result, excess milk will come out as a fountain in the form of vomiting. The strength of the secretions that will come out will depend on the amount of milk eaten and the pressure it creates in the stomach.
If such a phenomenon is observed extremely rarely, then parents need not worry. Another thing is if this type of ailment makes itself felt constantly. In this case, it is necessary to take measures to control food intake, and this is easy to do - using a regular bottle. After finishing the next procedure for feeding the baby, you need to hold him in an upright position for several minutes and watch him during this time. When the baby is in a horizontal position, the food he eats under the influence of the gag reflex can enter the respiratory tract, which can cause asphyxia.
If, while observing the child, you notice that vomiting is still present with a fountain, and the reason for its appearance is in no way connected with overfeeding, then in this case you should show it to the doctor. It is possible that there is a serious disease of an important organ here.
 What actions should parents take if the baby has diarrhea against the background of vomiting? The main thing is not to worry about this, because it is quite mild pathology which is very easy to identify and treat. If the baby has diarrhea, then most likely this is due to the penetration of a bacterium, infection or virus into the body. Faced with such a threat, the body will do everything necessary to remove the foreign body. It is the consequence of the struggle of the body with an external stimulus that is vomiting and diarrhea. Also, some newborns diarrhea may be the result of poisoning.
What actions should parents take if the baby has diarrhea against the background of vomiting? The main thing is not to worry about this, because it is quite mild pathology which is very easy to identify and treat. If the baby has diarrhea, then most likely this is due to the penetration of a bacterium, infection or virus into the body. Faced with such a threat, the body will do everything necessary to remove the foreign body. It is the consequence of the struggle of the body with an external stimulus that is vomiting and diarrhea. Also, some newborns diarrhea may be the result of poisoning.
In addition to the already indicated symptoms, the child may have a fever. It can also help at home without visiting a doctor to identify the disease at an early stage. Against the background of diarrhea and fever, the child often has a state of weakness, the skin turns pale and the lips dry up.
In a state where the baby has vomiting with diarrhea, the body temperature can rise to 39 degrees. From this we can conclude that qualified medical assistance is needed here. Very often in the summer months bacteria penetrate the children's body, causing poisoning. Therefore, if the baby has a fever against the background of vomiting and diarrhea, then this is a serious reason to show it to the doctor.
 If you notice vomiting in a child, then the first thing you need to figure out is whether this is a pathological process of excreting food from the stomach or is it just a normal regurgitation. Specialists have no treatment against vomiting, as it is nothing more than a symptom of a certain disease or pathology. In order to protect the child from vomiting in the future, reasons need to be established. that give rise to this phenomenon. And after these causes are eliminated, the child's health will return to normal, and he will no longer vomit.
If you notice vomiting in a child, then the first thing you need to figure out is whether this is a pathological process of excreting food from the stomach or is it just a normal regurgitation. Specialists have no treatment against vomiting, as it is nothing more than a symptom of a certain disease or pathology. In order to protect the child from vomiting in the future, reasons need to be established. that give rise to this phenomenon. And after these causes are eliminated, the child's health will return to normal, and he will no longer vomit.
What should parents do if they notice vomiting in a baby?
First you need to calm down. From this point on, carefully monitor the condition of the child. Pay attention to the composition of feces and shape. Still won't hurt you take a temperature measurement, by which you can also determine the state of health of the crumbs. And when you have all this information, you can go to the doctor and at the reception tell him about your observations.
 Vomiting in the baby can occur for various reasons. In most cases, it turns out to be ordinary regurgitation, and you should not worry about this if it manifests itself without a temperature. But when, in addition to this symptom, there are other unpleasant signs for the baby, for example, fever, diarrhea, this indicates that the child has a serious illness. In any case, if parents have doubts about what exactly is happening with the baby, do not be inactive. It is better to immediately go to the doctor for professional advice.
Vomiting in the baby can occur for various reasons. In most cases, it turns out to be ordinary regurgitation, and you should not worry about this if it manifests itself without a temperature. But when, in addition to this symptom, there are other unpleasant signs for the baby, for example, fever, diarrhea, this indicates that the child has a serious illness. In any case, if parents have doubts about what exactly is happening with the baby, do not be inactive. It is better to immediately go to the doctor for professional advice.
Vomiting refers to the situation in which the contents of the stomach and, sometimes, the intestines leave the body through the mouth. It occurs in people regardless of gender and age, often vomiting occurs in a child, which makes parents seriously worried.
There are many reasons why a baby may vomit. It can be caused by the following factors:
In some cases, vomiting in a baby does not cause concern - the regular rejection of a small part of food back into the oral cavity is called regurgitation. It is considered a variant of the norm up to a certain age and in the absence of other alarming symptoms.
 Feeding a child is a responsible task that requires care, especially when it comes to the baby in the first months of life. The norm of food intake is individual for each child, with artificial feeding The age-appropriate volume of the mixture may be too large for a particular baby. If the baby is fed with mother's milk, it is almost impossible to control the amount eaten. In response to exceeding the required volume of milk or mixture, vomiting occurs in the baby.
Feeding a child is a responsible task that requires care, especially when it comes to the baby in the first months of life. The norm of food intake is individual for each child, with artificial feeding The age-appropriate volume of the mixture may be too large for a particular baby. If the baby is fed with mother's milk, it is almost impossible to control the amount eaten. In response to exceeding the required volume of milk or mixture, vomiting occurs in the baby.
It is enough to simply determine that the contents of the stomach left it due to overeating:
If part of the food is rejected, you should reduce the portions of food for the baby and monitor the further condition. If, with a decrease in portions, the child continues to vomit after eating, there are good reasons to inform the doctor about this.
 If an infant has vomited in a fountain, it is most likely caused by problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, they begin to appear closer to the second month of the baby's life. These problems consist in regular vomiting about a couple of hours after feeding the baby. The amount of liquid released is usually greater than the amount eaten. Part of the milk in a folded form is overcooked, this is due to food retention in the stomach and its untimely entry into the intestines of the crumbs.
If an infant has vomited in a fountain, it is most likely caused by problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, they begin to appear closer to the second month of the baby's life. These problems consist in regular vomiting about a couple of hours after feeding the baby. The amount of liquid released is usually greater than the amount eaten. Part of the milk in a folded form is overcooked, this is due to food retention in the stomach and its untimely entry into the intestines of the crumbs.
The consequences of congenital pathologies may be the lack of weight gain or its loss, which requires careful observation of specialists and hospitalization if necessary.
With damage to the central nervous system, vomiting in infants can be regular. It usually manifests itself in the form of small, but frequent regurgitation, less often - rejection a large number food. Diseases that can cause this problem are as follows:
An appeal to a neurologist in case of frequent rejection of what has been eaten is necessary, because the neurological causes of this phenomenon must be treated as early as possible in order to achieve the desired result. As a rule, vomiting in infants with neurological diseases is accompanied by other signs of the disease:
It is important to detect a disease in the field of neurology at an early stage for the further full life of the child.
Unlike other causes, with infectious diseases, vomiting and fever in the baby are observed. All diseases caused by infection are divided into 2 groups:
Depending on the cause, additional problems may be found in the child.
A disease occurs due to pathogens entering the gastrointestinal tract of the child - bacteria and viruses that penetrate the oral cavity when the child tries to eat something dirty or suck on unwashed hands. In addition to vomiting in intestinal infections, the following signs of the disease are present:
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately call an ambulance. Frequent vomiting and liquid stool in infants, they can cause dehydration, which requires immediate fluid replenishment using droppers.
Often the appearance of vomiting in diseases of the child caused by various infections. It occurs with angina, SARS, pneumonia and otitis media. As a rule, with these diseases, vomiting appears in response to eating. In addition to her, the baby has a fever, general weakness, drowsiness, moody mood and lack of appetite. On examination, the doctor pays attention to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat. There is a cough.
More serious diseases, the first signs of which may be vomiting, are meningitis and encephalitis. With these diseases, vomiting is regular, the amount of rejected food is large. The baby screams loudly and for a long time, hides from bright light, seizures may occur.
With these symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance, as the disease can be fatal.
 Often, parents seek to introduce new foods into the baby's diet as soon as possible. The age at which the baby is ready to receive new food is different for everyone, the inscriptions on jars of mashed potatoes and grandmother's advice are not the main criterion for the introduction of adult products. When introducing new foods to the crumbs, you should carefully monitor his reaction. If vomiting occurs immediately after eating or after a while, you should postpone the moment of complementary feeding and continue to feed the baby with breast milk or formula.
Often, parents seek to introduce new foods into the baby's diet as soon as possible. The age at which the baby is ready to receive new food is different for everyone, the inscriptions on jars of mashed potatoes and grandmother's advice are not the main criterion for the introduction of adult products. When introducing new foods to the crumbs, you should carefully monitor his reaction. If vomiting occurs immediately after eating or after a while, you should postpone the moment of complementary feeding and continue to feed the baby with breast milk or formula.
A child who is already actively eating mashed foods may also be prone to vomiting. It can be caused by poor-quality food or violation of storage conditions. It should be noted that small deviations from the ideal quality of products are enough for a child to cause poisoning. It is defined by the following symptoms:
Frequent vomiting, diarrhea and elevated temperature you should call a doctor to resolve the issue of hospitalization, there is a risk of dehydration, which is very dangerous for the baby.
As a rule, when people talk about the treatment of vomiting, they mean ways to stop it. It makes no sense to treat vomiting, because it is not a disease, but just a sign of a disease. To alleviate the condition of the baby and protect him from serious consequences in the following ways:
Vomiting is often referred to as periodic regurgitation caused by air entering the stomach. If this happens infrequently, and the volume of vomit is very small, this is not a pathology and is considered normal, which is inherent in most babies. You can reduce the amount of spitting up as follows:
Sometimes vomiting appears with a sharp transition from breastfeeding artificial or when replacing one infant formula with another. In this case, you should cancel the replacement of power and make it gradually and carefully.
Regardless of the causes of vomiting in infants, it should be reported to the pediatrician to exclude pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and infectious diseases. If necessary, the doctor will advise you to visit a neurologist in order to exclude problems of the central nervous system of the child.
We're almost a month old. My baby has been vomiting for the second or third time after eating with a fountain. curdled milk or just milk. Maybe it's regurgitation, but it's painfully loud and forceful. No temperature. We are on GW. I ate a little ... After reading the article printed below, it seems to me that the reason may be the ingress of air during breastfeeding, she sucks several times and swallows air or a strong pressure of milk in her chest.
How to find out the cause and whether it is necessary to treat. Drink some water or rehydron? Call a doctor? We eat on demand, about every 3 hours.
What is regurgitation and vomiting in newborns? This is the reverse movement of the contents of the stomach into the mouth. In medicine, this phenomenon is called "Syndrome of regurgitation and vomiting." As a rule, this is not a disease, but just a sign of some kind of disease. Let's learn more about regurgitation and vomiting in newborns.
The strongest symptom of the disease is vomiting. Vomiting can begin in any person, regardless of age, and is accompanied by profuse salivation, increased heart rate, nausea, cold extremities and a pale face. During vomiting, the abdominal muscles, the diaphragm and the center of the brain work. A signal is sent to the brain and the stomach pushes the food out, i.e. into the mouth.
Regurgitation is a type of vomiting that occurs in newborns and in children under one year old. Only the abdominal muscles are involved in regurgitation, allowing food to pass out passively. Often, spitting up newborns is considered normal, but sometimes it can be a manifestation of many serious diseases. But vomiting cannot just start in healthy children. Remember this!
Distinguishing regurgitation from vomiting is easy. Gagging may continue for a long time, and regurgitation occurs only once immediately after eating or after an hour. During regurgitation, a child usually comes out with a small amount of milk or water, and when vomiting, bile is added to the contents and the color of the discharge becomes yellowish.
According to statistics, regurgitation occurs in more than 70% of healthy and sick children. The most frequent regurgitation occurs in the first weeks of a baby's life, and the older the child, the less they become, and by the year they finally disappear.
Here the reason lies in their anatomical features:
How to determine the rate of regurgitation in a newborn?
How do regurgitation and vomiting occur in children.
Regurgitation in newborns occurs immediately after eating or after an hour. They can also be copious or not, frequent or infrequent, and in some cases, accompanied by certain odors and hiccups. All this is considered normal. Although not, frequent and profuse spitting up in newborns can be harbingers of serious illness.
Some children spit up only at night. At such moments, there is a danger of food entering the respiratory tract, which can lead to the development of pneumonia.
As a rule, with frequent and profuse regurgitation and vomiting, dehydration occurs in a newborn. This is very dangerous for the life of the baby. Usually in such cases the child is hospitalized! In order to avoid a disastrous outcome, all parents, without exception, should be able to recognize dehydration of the body and, preferably, at a very early stage. To do this, it is enough to know the following:
If you find two or three symptoms from this list, immediately consult a doctor!
As mentioned earlier, regurgitation in newborns and vomiting are usually the result of an illness or pathology. Sometimes even the doctors themselves cannot identify their cause. I bring to your attention a small list of diseases and pathologies that cause regurgitation and vomiting in children.
The most dangerous causes of regurgitation in newborns:
Less dangerous causes of regurgitation in newborns:
If a child's regurgitation becomes suspicious, that is, frequent and profuse regurgitation, sometimes with a fountain or, even worse, with blood, then he must be examined in a hospital. More precisely, the child should be examined by a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, neuropathologist. Also, as necessary, it is desirable to conduct additional examinations: X-ray, ultrasound, FEGDS (examination of the esophagus and stomach with a thin tube that is inserted directly into the stomach), analysis of the acidity of the esophagus and analysis of feces for the presence of dysbacteriosis, etc. You may ask why A lot of everything? The fact is that there are a lot of reasons for regurgitation in newborns, and in order to recognize them, it is imperative to conduct a thorough medical examination of a sick child.
During regurgitation and vomiting, the child loses a lot of fluid and in order to avoid dehydration of his body, it is necessary to replenish the wasted water reserves in a timely manner. Therefore, in addition to food and breast (artificial) milk, additionally give the child a drink. Not only clean water is suitable here, but also soothing teas, for example, chamomile tea, compotes and fruit drinks. Also, you can buy a special ready-made mixture in a pharmacy, which helps to retain fluid in the body due to special components: rehydron, citroglucosolan and glucosolan. Dissolve the mixture according to the instructions.
Let the child drink it in small sips with breaks of 5-10 minutes and immediately after vomiting or spitting up about 50 ml. If the baby is very small and you can’t get him to drink, then use a pipette and drip into his mouth yourself.
If necessary, for example, with frequent regurgitation in a newborn, doctors sometimes prescribe therapeutic mixtures, for example, Nutrilon Antireflux and Frisof. They contain locust bean gum. It is gum that helps food pass into the stomach and does not allow it to return back. These mixtures begin to be given to a sick child, first in small doses (a couple of spoons) and gradually increase the volume, up to a positive effect. By the way, "Nutrilon antireflux" and "Frisof" can be given to children with difficult "stool".
However, medicinal mixtures do not always help, and then to baby food add Nutrilon OMNEO-2 or Lemolak. Or rather, they give instead of food. The first mixture is suitable if the child has regurgitation, intestinal colic, allergies and constipation. The second mixture - only with loose stools and regurgitation. Therefore, carefully read the instructions so as not to make mistakes in the mixtures. Otherwise, your mistake will only worsen the condition of the baby.
Again, if neither one nor the other therapeutic mixture has helped you, and the baby still has regurgitation, medication is prescribed. Remember - in no case, do not treat it yourself! All medicines can be given only after the permission of the doctor! Do not play with your child's health!!!
So, usually doctors prescribe antiemetics, vitamin A, B vitamins and other drugs, depending on the diagnosis.
What moms need to know when spitting up a newborn.
I can only say one thing - properly feed your child. After all, very often regurgitation in children begins just because of this reason, and you “wind” it around hospitals. Therefore, if the baby began to spit up, first of all analyze how you feed him. But this is only if his regurgitation is not frequent and not abundant !!! Here it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
What should mommy do if her baby is spitting up:
No less important is the very behavior of the parents when the child begins to spit up. So, if the baby burped, immediately raise him to a vertical position. This will help move the remaining food out of your mouth and prevent it from entering your airways. Many doctors often recommend putting the baby on the tummy for prevention. That's right, but never leave him alone at such moments. Unfortunately, more than half of child deaths are due to this.
And now a little about prevention.
To prevent frequent regurgitation in a newborn, follow the above feeding rules, feeding regimen, choose the right mixture, treat diseases such as dysbacteriosis, intestinal colic, constipation, loose stools, etc. in a timely manner.