
A cold is always an unpleasant event. It causes a lot of problems, but a cold is especially dangerous when breastfeeding. What to do if mom gets sick? Will this affect the baby's body? Will the drugs harm him? And is it possible to breastfeed a child with ARVI? The answers are in this article.
Previously, a sick parent was separated from her child and forbidden to feed him milk. But it is now known that mothers cannot stop lactation. With mother's milk, the baby receives all the necessary substances. Even if mom can infect him, the cold will go away easily.
Previously, a woman had to be careful during a cold and choose the right remedies. Now there is no urgent need for this, since they have begun to produce safe medications for colds. But you don’t need to relax anyway: if your mother is sick, she needs to be properly treated. You should also try not to infect the baby.
Forbidden:
If a young mother is sick, the baby should also be fed milk carefully. The drugs reach high concentrations two hours after administration. A small portion of these medications are passed through breast milk. It is better to plan treatment and feeding in advance, or pump.

It is much easier if the baby is already given complementary foods. Then you can increase the time by 3-4 hours. During a cold, there are no special prohibitions on medications, but it is still important to be careful:
Sometimes the mother's condition worsens. ARVI is especially dangerous when breastfeeding.

You have to use products that are prohibited during breastfeeding. In this case, it is advised to express milk every 3-4 hours. But there is no need to stop feeding your baby milk. Don't be afraid to infect him.
There are many prohibited drugs during lactation, so it is better to familiarize yourself with those that are not prohibited from taking. It is better to immediately have a list of the necessary medications at hand. If a mother is sick, it will be easier for her to choose treatment for herself. At the same time, care should be taken not to infect the baby. But if the situation is critical, only consulting a doctor will help.
Drugs that are allowed to treat colds while breastfeeding:
Old well-known methods are also not prohibited: rubbing, herbal compresses, cupping, herbal infusions are good for treating ARVI during breastfeeding. Foot baths with herbs help. Mustard plasters will not be superfluous. If the cough is very severe, herbal inhalations will help. You can use both the old method with potatoes and modern methods - nebulizers.
Sometimes even folk remedies may cause allergies in the child. Therefore, they must be used carefully.
During a cold, a nursing mother is advised to drink more herbal infusions. Plantain, raspberry and currant leaves help well. Tea can be brewed in a thermos and drunk in small sips throughout the day.

To prevent a cold, a mother needs to monitor her health, as well as the health of her baby.
A cold can take a nursing mother by surprise. With the onset of cold weather and the off-season, the risk of colds and flu is very high. Having discovered the first symptoms, many mothers panic and are afraid to breastfeed their baby in order to protect him from the disease. But is this justified?
Doctors are categorically against stopping breastfeeding during mother's illness, unless treatment with drugs contraindicated during lactation is required. Colds are usually caused by viruses and are seasonal. For a viral infection, treatment with antibiotics is not carried out unless there is a bacterial infection. Therefore, there is no reason to stop breastfeeding.
If it becomes necessary to treat the condition with antibiotics, tell your doctor that you are breastfeeding. You will be given medications approved for use during the lactation period.
Mother's milk is a source of nutrients for the child, as well as a powerful immunological protection for his body. Women's milk contains proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, amino acids, protects the child's body from bacteria and viruses due to the immune factors included in the composition, promotes the growth and proper development of organs and systems, as it contains special hormones.
Infant formulas, although close in composition to breast milk, still cannot completely replace it. Breast milk substitutes do not contain substances that provide immune protection and do not contain growth hormones.
When a baby is suddenly switched to formula, his mental state and immune system suffer, which suddenly loses support. During this period, children's unformed immunity becomes defenseless against attack from viruses and bacteria from the outside. It is very easy to get sick at such a moment: the stress of losing close contact with the mother and unusual food reduce the protective functions of the young body.
There are several misconceptions about breastfeeding during illness, let's look at the most common:
This is an incorrect statement. We all know that colds and flu are transmitted through airborne droplets from coughing, sneezing, etc. A less common route of transmission is through household contact, in which infection occurs through contaminated household items (dishes, door handles, switches) and handshakes. Yes, there are diseases in which the virus can be transmitted to a child through breast milk (HIV, Ebola, etc.), but with colds, only virus particles that are neutralized by the mother’s immune system are found in the milk.
Also fictional. According to medical research, body temperature does not affect the quality of breast milk.
This is absolutely true, but there is no need to be scared and refuse treatment. There are many medications that can be combined with breastfeeding. You just need to consult your doctor before use.
In the treatment of colds, you can use “folk methods” that alleviate the condition and are safe for the child.
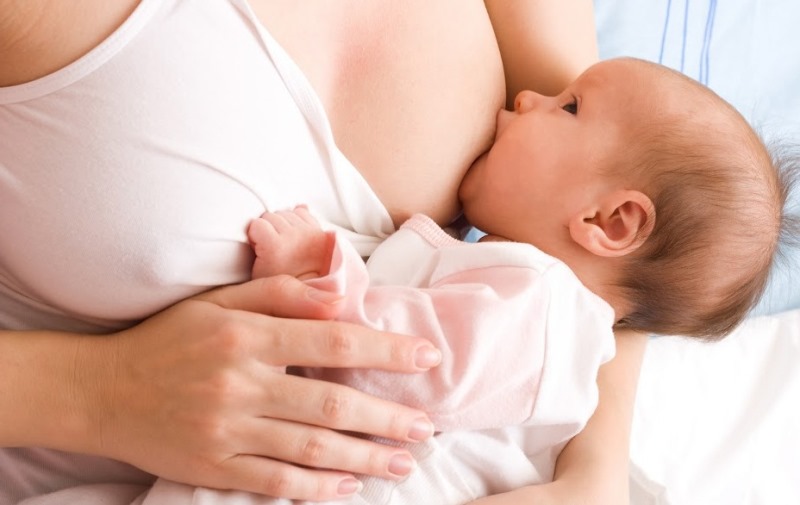

Breastfeeding during a cold should be carried out according to the child’s usual schedule. If you follow preventive measures, you can protect your child from infection.
Most often, the body of a healthy adult person copes with a cold on its own, without the use of medication. To do this, you need to maintain bed rest and peace of mind, then the immune system will cope on its own. Of course, for mom infant It is quite difficult to follow these recommendations and she cannot do it without outside help.
Colds need to be treated promptly, and treatment methods depend on the symptoms:
When treatment does not bring relief and the condition worsens, call a doctor! Perhaps it is not a cold, but a more serious illness.
You should only stop breastfeeding when serious treatment is needed. Your doctor will warn you about this.
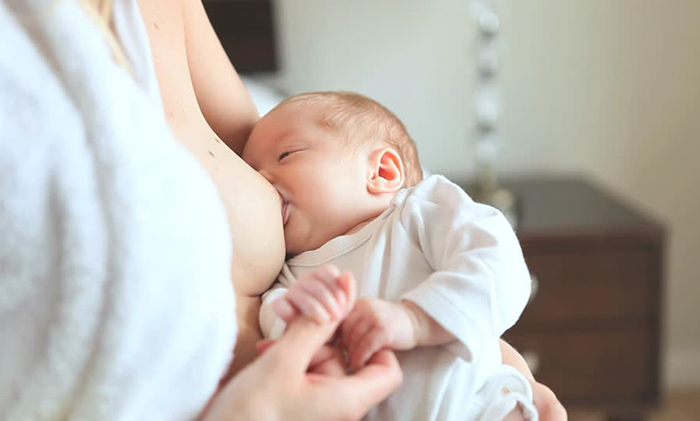

During the height of the disease, when the possibility of infecting people around you is highest, it is important to take measures to eliminate the virus in order to protect your child and the rest of the household.
It is important to maintain close contact with your baby so that he does not feel abandoned: during feeding, stroke him gently, talk to him and sing songs if possible. Just remember to wear a gauze bandage.
Treating colds and breastfeeding are compatible activities today. Stopping breastfeeding will cause more harm to the child's health than a small concentration of drugs entering the child's body with milk.
A cold is always an unpleasant event, especially when breastfeeding. In addition to high fever, runny nose, cough and weakness, there is also concern about the child. A nursing mother immediately wonders whether it is possible to continue breastfeeding during ARVI or flu, and whether the baby will get sick.
A few decades ago, doctors recommended isolating the child from the mother and stopping feeding breast milk with a similar disease. However, now doctors categorically reject this method. After all, weaning will reduce the baby’s immunity much more than a cold!
A nursing woman who has a cold should continue to give her baby breast milk. You should refuse only if you are taking medications that are dangerous for your baby.
The earlier you detect the disease, the better. Main symptoms of a cold:
If you treat a cold correctly, it will go away in 7-10 days. To easily overcome the disease and not harm your child, follow a number of rules.

Folk remedies for colds while breastfeeding - safe and effective treatment. Inhalations that are used using boiled potatoes are considered the most harmless. But you can breathe not only over boiled potatoes. Will be a good remedy essential oils.
![]()
A few drops eucalyptus drop some boiling water into a kettle and place a funnel in the spout of the kettle. The funnel can be made from cardboard or thick paper. Inhalations will clear the airways, relieve a runny nose, alleviate sore throats and increase tone.

Useful for respiratory diseases onion and garlic. However, experts do not recommend consuming spicy foods while breastfeeding, or at least delaying introducing them into the diet until the baby is six months old.
Another useful and harmless remedy - foot baths. Take baths with mustard powder added before bed. After the procedure, be sure to wear woolen socks and wrap your feet in a blanket.
Drinking plenty of fluids and wiping the body with a weak solution of vinegar will help lower your temperature and improve your well-being.

There are pills and other medications that you can start using without consulting a doctor.
You can safely take Grippferon for colds while breastfeeding. It is easily tolerated by the body and has no contraindications during lactation.
Paracetamol will be an excellent antipyretic and safe remedy. Studies have proven that the tablets are quickly absorbed and reduce fever. At the same time, they are also quickly eliminated from the body, which is so important during breastfeeding.
Remember that you should not abuse medications. And at a temperature above 38 degrees, be sure to consult a doctor.

In this case, topical medications will help, including Hexoral and Strepsil. For severe coughs, use expectorants such as Lazolvan or Ambroxol. To relieve pain in the respiratory system, doctors recommend syrups with a herbal base (Chest Elixir or Doctor Mom)
When breastfeeding, medications containing Bromhexine are strictly prohibited! Such medicines are an excellent replacement for herbal preparations.

It is better to treat a runny nose with plant-based drops, like Pinosol. Sprays containing sea water (Salin) are also suitable. At severe congestion use drops that constrict blood vessels (Navizin, Farmazolin, Tizin).
Do not overuse drops under any circumstances! These drugs are often addictive. In addition, they can cause arthophic rhinitis.
Correct dosing – main principle during the treatment of colds during lactation. If the listed remedies do not help within seven days and the temperature does not subside, be sure to consult a doctor!
Breastfeeding mothers often develop colds and acute respiratory viral infections. This is due to the fact that the immunity in their body is weakened as a result of birth stress, hormonal changes, overwork and lack of sleep. This is where a lot of questions arise: whether to feed a child during illness or stop breastfeeding, what and how to treat, how to protect the baby from illness.
Previously, it was advised to definitely stop feeding the baby. Currently, this tactic is recognized as incorrect: along with milk, the baby will also receive ready-made antibodies to viruses or bacteria, and therefore, even if it is not possible to protect the child from the disease, the disease will occur in a milder form.
But you still need to try to take preventive measures so as not to infect the baby:
You can also consult with your pediatrician about preventing the disease in your child.

At the first sign of ARVI, a nursing mother should immediately consult a doctor.
The maximum concentration of the drug in breast milk is reached 2 hours after taking it. That is why, in order to minimize the intake of the drug through the baby’s milk, you can feed the baby and express milk for the next feeding, and then take the medicine.
Expressed milk does not need to be boiled so that it does not lose its quality. The baby should be fed with a spoon, and not with a bottle with a nipple, so that the child does not give up the more labor-intensive sucking of the breast.
If, during a severe infection, there is a need to use drugs that can have a negative effect on the child, then temporarily, on the advice of the pediatrician, the baby is spoon-fed. But all this time, the mother expresses her milk every 4 hours in order to maintain lactation and return to it after the end of treatment.
If a nursing woman has a cold, she can be treated with medications or traditional methods. The necessary medications must be selected by a doctor. Symptomatic treatment is carried out to eliminate the main manifestations of the disease - fever, runny nose, cough, sore throat and headache.
For treatment, the following medications can be used during breastfeeding:
But drugs from the tetracycline group, Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin, sulfonamide drugs (Biseptol, Bactrim, etc.) are strictly prohibited.
If you are prone to allergies, Suprastin and Tavegil can be prescribed.
In addition to drug treatment, you can use mustard plasters, rubbing chest warming ointments. Inhalation with alkaline mineral water “Borjomi” using a nebulizer helps to remove phlegm.

Together with the milk of a mother who has fallen ill with ARVI, the baby receives antibodies to the virus, which minimizes the risk of infection. In addition, many modern medications are compatible with breastfeeding, so in the vast majority of cases the child does not even need to be temporarily weaned.
Treatment according to traditional medicine prescriptions should also be carried out with caution, since most recommendations suggest the use of decoctions from plant materials, which can cause allergies in the child (or mother).
Drinking plenty of fluids, which is necessary in the treatment of colds, can be achieved by consuming decoctions of chamomile, plantain or birch leaves, and linden blossom. Tea made from leaves or twigs of currants and raspberries will have a beneficial effect. A rosehip decoction will provide the body with vitamin C, which helps cope with infection.
There are means for safe treatment of colds and acute respiratory infections in women during breastfeeding. There are quite a lot of drugs that are harmless to the baby and effectively relieve the mother of the disease. But you can’t self-medicate or select medications. The doctor will take into account the need to prescribe each drug and select a safe dose.
There is no need to stop feeding your baby. With milk, the baby will receive antibodies against pathogens that will help him cope with the disease if it was not possible to protect the child and he became infected from his mother.
The time when a child is breastfed is special, incomparable. This is the time when mother and child are as close as possible. Breastfeeding is healthy and enjoyable for both. And suddenly…. mom got sick. What to do in this situation? Very often, people around you recommend stopping breastfeeding, arguing that the disease will be passed on to the baby. If the mother continues to feed the child, then it is advised not to use medications. There are suggestions to express and boil the milk, and only then give it to the child. This is a completely wrong opinion! People who give such advice (and often insist on their implementation) have absolutely no understanding of the topic of breastfeeding.
2 165278
Photo gallery: Is it possible to breastfeed if your mother is sick?
So, is it possible to breastfeed if your mother is sick? Before deciding on further actions, you need to understand why your mother got sick and what treatment is required.
A breastfeeding woman who has contracted a common viral infection (or, in other words, a cold) should not stop breastfeeding. After all, the baby received the infection even earlier than the mother felt the first clinical signs of the disease. His body receives protective antibodies from his mother's milk. And if you interrupt feeding at this stage, the baby will be deprived of the immune support he needs at the most difficult moment. He is left alone with viruses, having no experience of fighting them. The chances of such a baby getting sick increase significantly.
For a mother who has weaned her baby, things are no better. At elevated temperature It is very difficult to tolerate pumping 6-7 times. It is not always possible to fully express milk in such a situation, and this threatens stagnation of milk and possible mastitis, which will only worsen the situation. It is the baby who is best at emptying the breasts of milk. But milk does not change at high temperatures. Its taste does not become rancid, it does not curdle or sour. But boiling milk destroys most protective factors.
A nursing woman can reduce her temperature with paracetamol-based medications or with paracetamol itself. But use them only in cases where the temperature is poorly tolerated. If you can be patient, then it is better to let the body fight viruses on its own, because an increase in temperature is a kind of protection that inhibits the proliferation of viruses. And under no circumstances use aspirin.
Viral infections usually require symptomatic treatment compatible with breastfeeding. These include gargling, inhalation, and using cold remedies. Antibiotics are not usually prescribed.
Antibiotics are required for a nursing mother for diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms (sore throat, pneumonia, otitis media, mastitis). Currently, it is not difficult to choose antibiotics that will be compatible with breastfeeding. These can be antibiotics from the penicillin series, many macrolides and first and second generation cephalosporins. But it is better to avoid antibacterial drugs that affect bone growth or the process of hematopoiesis (chloramphenicol, tetracycline, fluoroquinolone derivatives, etc.).
Antibiotics can provoke the development of dysbiosis, or disturbances of intestinal microbiocenosis. Special treatment is usually not required, because breast milk contains factors that promote the growth of normal microflora and suppress pathogenic ones. Artificial feeding can also cause dysbiosis, and it will be more difficult to cope with it. And for prevention, both mother and child can take special medications to maintain normal intestinal microflora.
Infectious diseases, as a rule, make it possible to select drugs that are completely compatible with breastfeeding. And homeopathy and herbal medicine will always have your back.
WHO recommends herbal treatment over drug therapy. If you cannot do without it, then you need to choose drugs that have less negative impact on the child. It is best to take medications during feeding or immediately after it, so that the child does not eat during the maximum concentration of the drug in the blood and milk. Breastfeeding should be interrupted only if absolutely necessary. In this case, lactation should not stop.
Sufficient milk production is maintained by pumping the breast 6-7 times a day (with mature lactation). After 2-3 weeks, or at most a month of weaning, the baby himself will restore the number of feedings he needs.
Finding out the compatibility of a medicine with breastfeeding is now not difficult. First, tell your doctor that you are a nursing mother. Secondly, check your doctor’s prescriptions by referring to special reference books. Most doctors have them, necessarily the head of the department, and in any pharmacy. And the annotation usually indicates whether it is possible or contraindicated to breastfeed while using this drug.