

Breast enlargement can occur due to the growth of ducts and glandular tissue or due to fatty deposits. If the breast increases due to the growth of glandular tissue, then gynecomastia is considered true, and the increase in breast volume due to fatty deposits is false gynecomastia.
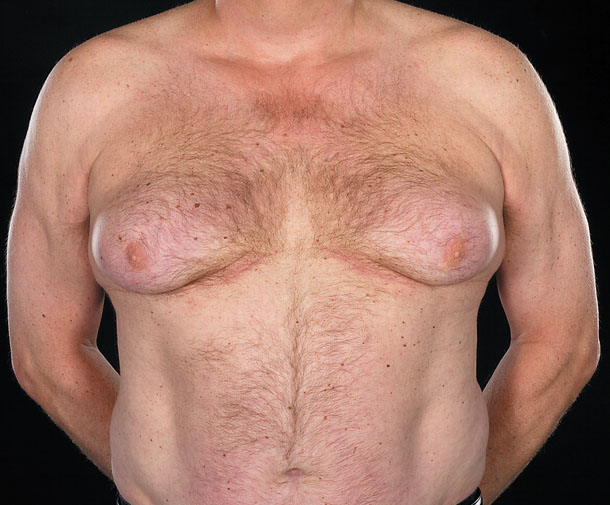
The severity of breast enlargement can be different - from 1 to 10 cm, and capture one or both mammary glands. More often there is a symmetrical lesion of both mammary glands at the same time, an increase in only one breast with gynecomastia is quite rare. Enlarged mammary glands with gynecomastia usually look like slightly pendulous female breasts small size.
The development of gynecomastia of any kind is based on an imbalance of sex hormones with a predominance of estrogens. That is, any diseases, drugs, and other items that can lead to the fact that estrogen in the body of a man will be more than testosterone, can cause gynecomastia.
The fact is that the predominance of estrogens leads to the fact that they begin to act on tissues that are sensitive to them, which include the ducts of the mammary glands. Under the influence of estrogen, breast tissue, which in men is in its infancy, begins to actively grow, forming a breast. That is, there is a process similar to what is happening in the body of young girls during puberty, when their breasts begin to grow, the pelvic bones increase, etc.
Normally, breast formation does not occur, since estrogens present in the body of a man do not have an activating effect on breast tissue for two main reasons. Firstly, there are very few estrogens, so their effect on the glandular tissue of the breast is not able to bring the latter out of its embryonic state in which it is located. Secondly, estrogens are suppressed by a large amount of testosterone, which is produced in the body of a man and determines the characteristic sexual characteristics. But if for some reason the amount of estrogens increases, and they begin to prevail over testosterone, then the growth of tissues that are normal in the male body in its infancy is activated. As a result, the feminization of a man occurs, that is, female sexual characteristics appear, which include the breast.
Thus, gynecomastia develops if estrogens predominate over testosterone in the body of a man. Moreover, the cause of hormonal imbalance is not important, since gynecomastia is triggered precisely by an increase in the content of estrogens relative to testosterone.
During gynecomastia, three successive stages are distinguished, such as proliferating, intermediate And fibrous. At the stage of proliferation, the process of growth of the ducts and glandular tissue of the mammary gland takes place, which lasts an average of 4 months. Further, in the intermediate stage, lasting 4-12 months, the maturation of the mammary gland occurs. In the fibrous stage, dense connective tissue and fatty deposits appear in the mammary gland, which completes the complete formation of the organ. Accordingly, during the first 4 months, a person notices that his chest is growing, and then fixes its compaction.
Treatment for gynecomastia can be conservative or surgical. In all cases, first resort to conservative therapy, which allows you to stop the progression of the process and in many situations to achieve complete "resorption" of the already formed breast. Surgical treatment of gynecomastia is carried out only if there is a tumor formation in the mammary gland or the man is not satisfied with the appearance chest for aesthetic reasons. If there is a gynecomastia operation in the mammary gland, it is mandatory. But operations to remove the breast for aesthetic reasons are not always performed, since in many cases the appearance of the chest after surgery may be even worse than before.
Conservative treatment, started in the proliferating stage, allows to achieve complete involution and disappearance of the breast, since all changes are still reversible. Conservative treatment, started at an intermediate stage, can only stop the progression of the process, but to achieve reverse involution and the disappearance of an already grown breast is possible only in rare cases. Conservative treatment at the fibrous stage also only allows you to stop the progression of the process, but it is impossible to achieve the disappearance of the breast under any circumstances with its help. This means that in order to eliminate the formed breast, you will have to resort to surgical intervention, during which the glandular and adipose tissue is removed.

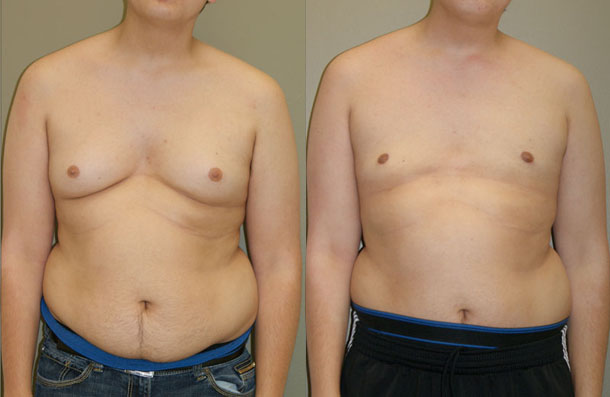
This photo shows a man with severe gynecomastia.
Some scientists and doctors distinguish only two main types of gynecomastia - true and false, and physiological and idiopathic are classified as true variants. However, in world practice, the above version of the classification is used. We consider these differences between the classifications to be not fundamental, since regardless of whether idiopathic and physiological gynecomastia are included in the true composition or are distinguished into separate varieties, their essence and characteristics are unchanged. In order to avoid classification confusion, we will consider the characteristics of all types of gynecomastia in separate subsections with the corresponding names.
So, the following variants of physiological gynecomastia are distinguished, which occur in different age periods in males:
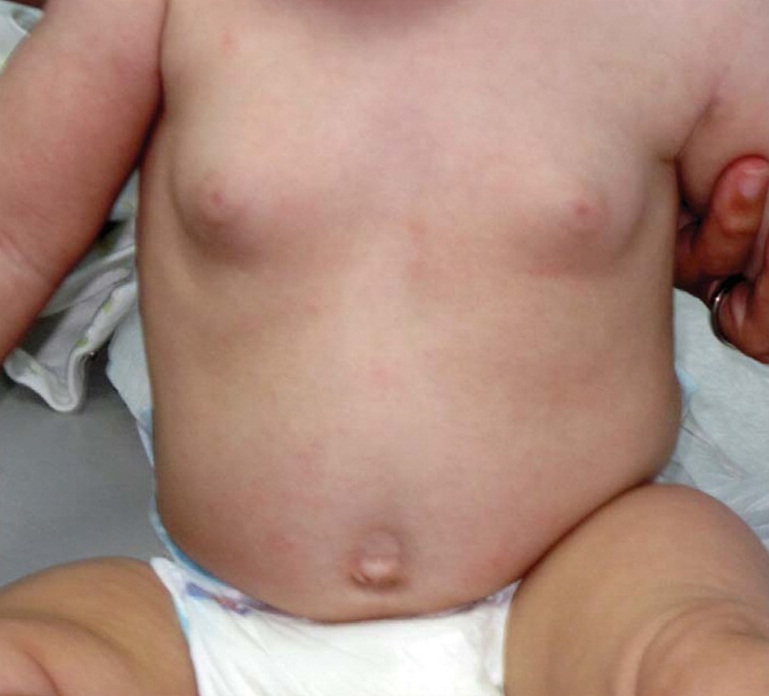 Gynecomastia in newborns appears in infants-boys of the first days of life and resolves on its own within 2 to 4 weeks. Gynecomastia is usually observed in 60 - 80% of newborn boys and is caused by exposure to maternal estrogens that penetrated to him through the placenta. When all the estrogens that entered the baby's blood from the mother's body during pregnancy are utilized, gynecomastia will disappear, and the mammary glands will involute, turning into completely flat formations with protruding small nipples.
Gynecomastia in newborns appears in infants-boys of the first days of life and resolves on its own within 2 to 4 weeks. Gynecomastia is usually observed in 60 - 80% of newborn boys and is caused by exposure to maternal estrogens that penetrated to him through the placenta. When all the estrogens that entered the baby's blood from the mother's body during pregnancy are utilized, gynecomastia will disappear, and the mammary glands will involute, turning into completely flat formations with protruding small nipples. This type of gynecomastia is a variant of the age norm, it resolves on its own within 1 to 2 years and does not require treatment. However, if after 2 years the gynecomastia has not gone away, then it is called persistent, it is considered pathological and, accordingly, requires treatment.
Unfortunately, the exact causes of teenage gynecomastia are currently unknown. However, it is known that in the early stages of puberty in boys, estrogens are produced in greater quantities than testosterone, which is the trigger for the development of temporary gynecomastia. As long as estrogens prevail over androgens in the body of a young man, he will have gynecomastia. But when the balance of hormones returns to normal, involution will occur and the grown breast will subside.
In principle, teenage gynecomastia is not a pathology, but can be the cause of serious psychological and sexual disorders in a teenager who is afraid because of the "wrong" appearance. Therefore, a boy suffering from gynecomastia needs psychological help and moral support for the entire period until his body returns to normal. However, parents should remember that if a boy has no other signs of puberty against the background of gynecomastia (hair growth on the body, armpits, pubic hair, voice change, etc.), then breast enlargement is a symptom of severe endocrine diseases, such as hormone-producing tumors of various localization.
Senile gynecomastia develops in men aged 55 - 80 years due to a decrease in testosterone production. Due to the decrease in testosterone levels, estrogens begin to prevail, as a result of which gynecomastia develops. As a rule, there is an increase in both breasts. Involution of senile gynecomastia is rare, but this condition is a variant of the norm, so it is almost never treated.
As a rule, false gynecomastia develops against the background of the general and can be expressed significantly.
 True gynecomastia is an increase in the mammary glands due to the growth of glandular tissue and ducts, is a pathology and requires treatment. True gynecomastia develops when estrogens prevail over androgens in the body of a man. However, hormonal imbalance is only a triggering factor and providing the necessary conditions for the growth of glandular tissue and breast growth. Accordingly, the causes of gynecomastia are factors that cause hormonal imbalance. And the reasons that cause hormonal imbalance with the prevalence of estrogen levels over androgens are very diverse, and therefore the range of factors that can lead to true gynecomastia is wide.
True gynecomastia is an increase in the mammary glands due to the growth of glandular tissue and ducts, is a pathology and requires treatment. True gynecomastia develops when estrogens prevail over androgens in the body of a man. However, hormonal imbalance is only a triggering factor and providing the necessary conditions for the growth of glandular tissue and breast growth. Accordingly, the causes of gynecomastia are factors that cause hormonal imbalance. And the reasons that cause hormonal imbalance with the prevalence of estrogen levels over androgens are very diverse, and therefore the range of factors that can lead to true gynecomastia is wide. It is currently established that The following factors can be the causes of true gynecomastia:
However, it is wrong to call breast growth in women gynecomastia. Indeed, in women, fat is deposited in the mammary glands during their life, connective tissue grows, the number of glands increases during pregnancy, which can lead to natural breast enlargement. It is these completely normal and physiological processes that are unreasonably and incorrectly called "gynecomastia". But women should remember that they do not have gynecomastia.
The fair sex has completely different diseases of the mammary glands, which in no way correlate with breast growth, so you should not be afraid of just breast enlargement that is not combined with any other symptoms of trouble in the body. And too large breast size in women is not called gynecomastia, but hypertrophy.
 So, the following factors can be the causes of true and idiopathic gynecomastia:
So, the following factors can be the causes of true and idiopathic gynecomastia: 1.
Tumors localized in the testicles, liver, lungs.
9. Tumors of the adrenal glands (adenoma, carcinoma).
10. Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex.
11. Dystrophy on the background of starvation or obesity.
12. Exposure to radiation.
13. Disorders of the hypothalamus (dysregulation of the adenohypophysis, etc.).
14. Diseases in which the function of the pituitary gland is impaired:
When palpated, the mammary glands can be dense, with nodular formations inside. Also, when feeling the chest, a slight soreness can be felt. The overgrown breast tissue is tightly fixed to the pectoral muscles and skin, so attempts to move the seal in any direction or pull the skin over them are useless. In rare cases, colostrum-like fluid is secreted from the nipples in gynecomastia. Also, sometimes men feel a feeling of pressure in the mammary glands and discomfort when clothes rub against the nipples.
In the clinical course of gynecomastia, there are three successive stages:
Depending on the size of the mammary gland, gynecomastia is divided into weak, moderate And expressed. To determine the size of gynecomastia, the circumference of the mammary gland and its height are measured, after which the index is calculated. If this index is less than 6, then gynecomastia is weak, index 6 - 10 - moderate gynecomastia, index more than 10 - pronounced.
For the treatment of pathological and idiopathic gynecomastia, conservative and surgical methods are used. Conservative treatment should be comprehensive and aimed simultaneously at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked gynecomastia and at stopping the effects of estrogens. Often, when the underlying disease cannot be treated (for example, taking medications, etc.), gynecomastia is treated with drugs that suppress the effects of estrogens. Surgical treatment is resorted to only if conservative therapy has been ineffective for 2 years of its implementation, and the person insists on the complete removal of the grown mammary glands for cosmetic reasons.
If gynecomastia is caused by a tumor formation in the mammary gland, then the only method of therapy is used - an operation to remove the neoplasm.
It is strictly forbidden to squeeze the mammary glands with tight bandages in order to stop breast growth, since this is not only ineffective, but also dangerous due to blood flow disturbances.
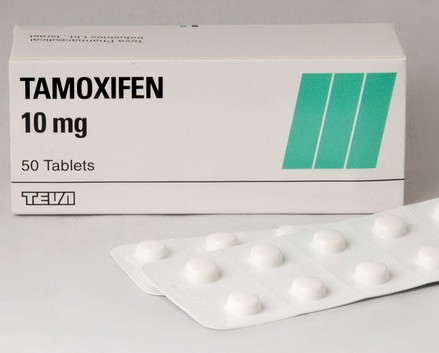 If gynecomastia is caused by a high level of estrogen, then anti-estrogenic drugs, such as Tamoxifen, Clomiphene, Danazol, are used to treat it. In addition, in addition to antiestrogen, drugs from the aromatase inhibitor group, such as Testoplakton or Thiamine bromide, are used for therapy. In addition to drugs that suppress estrogen activity, injections of B 1 and Aevita are used in periodic courses lasting 20 days. Both antiestrogen and aromatase inhibitors are used in long-term courses for a maximum of 2 years. If after 2 years a satisfactory result of conservative therapy has not been obtained, then surgical treatment of gynecomastia is performed.
If gynecomastia is caused by a high level of estrogen, then anti-estrogenic drugs, such as Tamoxifen, Clomiphene, Danazol, are used to treat it. In addition, in addition to antiestrogen, drugs from the aromatase inhibitor group, such as Testoplakton or Thiamine bromide, are used for therapy. In addition to drugs that suppress estrogen activity, injections of B 1 and Aevita are used in periodic courses lasting 20 days. Both antiestrogen and aromatase inhibitors are used in long-term courses for a maximum of 2 years. If after 2 years a satisfactory result of conservative therapy has not been obtained, then surgical treatment of gynecomastia is performed. If gynecomastia is caused by a partial deficiency of androgens, then testosterone and human chorionic gonadotropin preparations are used for treatment in combination with Galidor. In addition, to enhance the effect of hormonal drugs, it is possible to additionally include drugs that improve cerebral circulation (Cavinton, Cinnarizine, Actovegin, etc.), vitamins and metabolites (vitamin B 6 , ATP, glycine, etc.) in complex treatment.
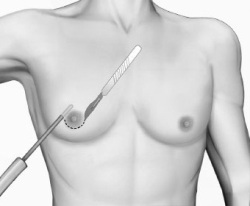 An operation to remove gynecomastia is performed only in case of failure of conservative therapy and, if the patient wishes, to remove the enlarged mammary glands. At the same time, it must be remembered that the chest after the operation may look even worse than before it, therefore, when deciding on the surgical removal of the mammary glands, everything should be carefully considered and weighed. To maximize the likelihood of a successful outcome of the operation, it is necessary to carefully select a surgeon who has experience in performing just such surgical interventions.
An operation to remove gynecomastia is performed only in case of failure of conservative therapy and, if the patient wishes, to remove the enlarged mammary glands. At the same time, it must be remembered that the chest after the operation may look even worse than before it, therefore, when deciding on the surgical removal of the mammary glands, everything should be carefully considered and weighed. To maximize the likelihood of a successful outcome of the operation, it is necessary to carefully select a surgeon who has experience in performing just such surgical interventions. Currently, the following types of operations are performed to remove gynecomastia:
In men, as in women, there are diseases of the breast. The most common of these is gynecomastia, the symptoms of which are an increase in the size of one or both mammary glands, pain when touched, the appearance of seals of various sizes, in rare cases, there is a release of fluid from the nipple.
This pathology develops as a result of the growth of fatty or connective tissues. The disease is benign, but with untimely treatment, it can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
The disease affects males of all ages, from infancy. The main cause of the disease is changes in the hormonal background, in particular an increase in the level of estrogen (the female sex hormone). Normally, its amount should not exceed a thousandth of a percent. Some factors lead to hormonal imbalance:
These reasons lead to the appearance in men of a breast similar to a woman's due to an increase in the number of glandular tissues.
Pathology of the mammary glands is also caused by some diseases that are not associated with the hormonal background:
Quite often, signs of this disease are found in men who combine sports with steroids. A sharp rejection of them leads to a temporary increase in the breast (the period can last from a week to several years).
The growth of breast tissue provokes the intake of certain medications: antibiotics, hormone-containing drugs, antidepressants.
The first suspicions about health problems appear after an increase in the mammary glands. As a rule, a neoplasm in the breast reaches from 2 to 10 cm in diameter. 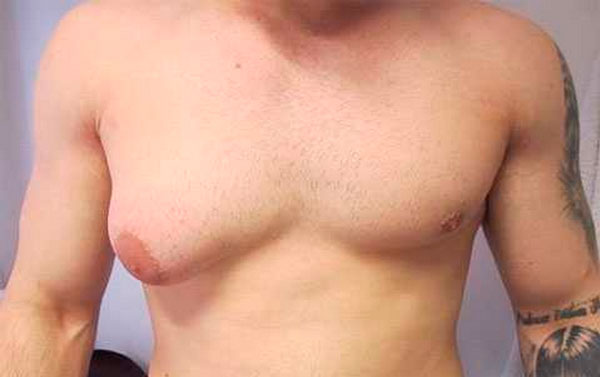
Most often, the disease affects infants and boys during puberty. Between the ages of 30 and 40, gynecomastia is less common. After 50 years, such a pathology in men is associated with significant physical inconvenience, requiring urgent treatment.
In some cases, the disease goes away without medication after the restoration of the hormonal background. If for more than 12 months the condition of the mammary glands worsens, it is necessary to start taking medications or resort to surgery. 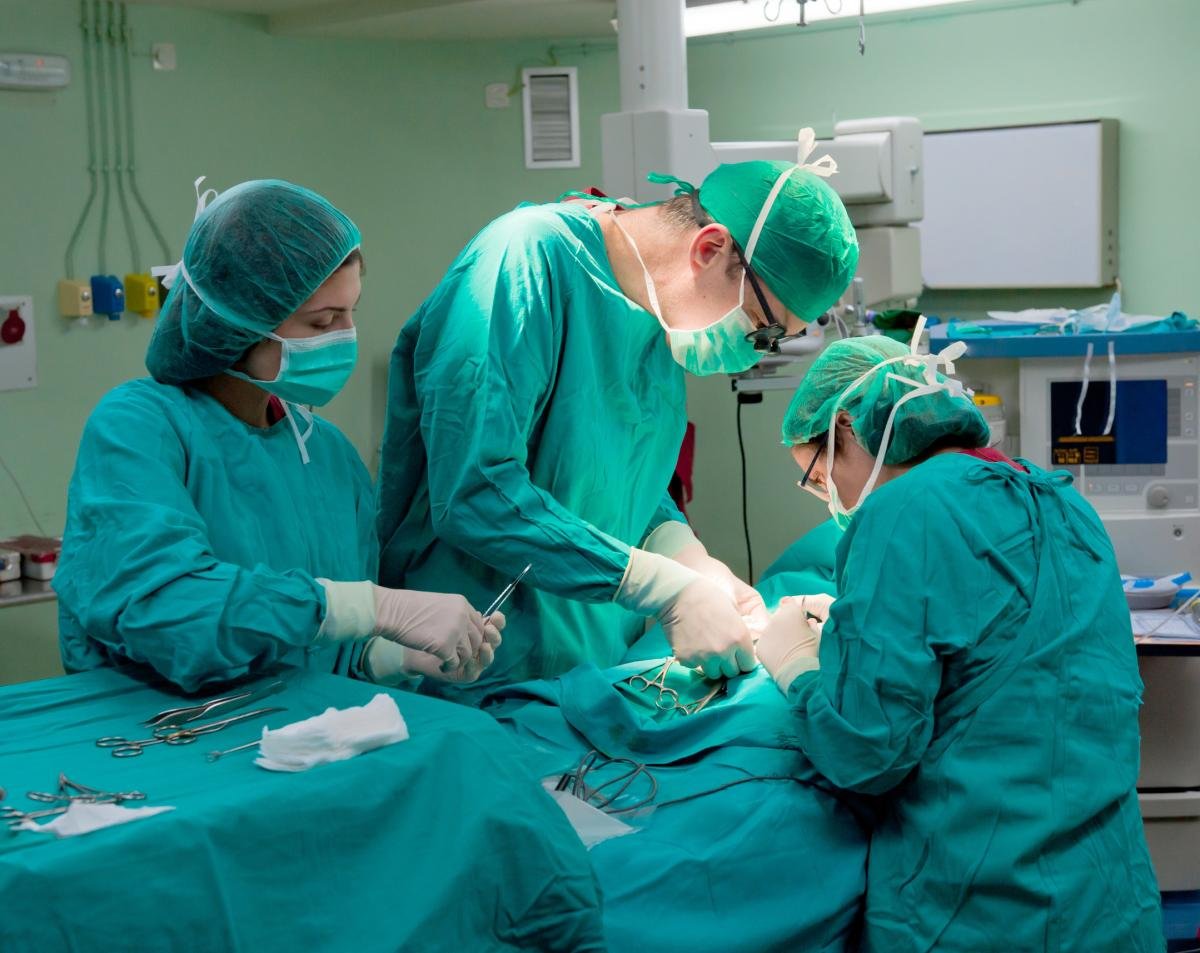
Symptoms of gynecomastia directly depend on the stage of the disease:

To prevent the degeneration of gynecomastia into cancer, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first suspicious signs.
Gynecomastia affects the male population at any age - from infancy to adulthood. Signs and course of the disease differ in patients of different ages.
An increase in the size of the mammary glands in newborn boys occurs in more than half of the cases. It is caused by physiological factors or pathological changes in the child's body. 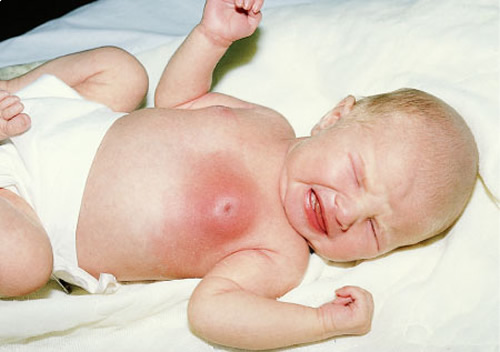
Gynecomastia in children is caused by:
Symptoms of gynecomastia in babies:
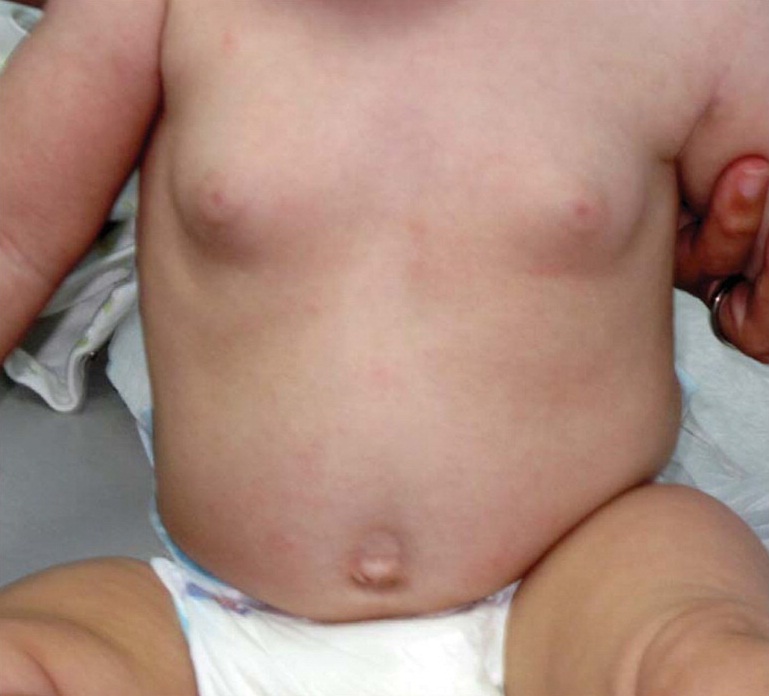
The disease, provoked by the peculiarities of physiology, does not need special treatment, in most cases the symptoms disappear after a few days. Pathological changes leading to changes in the mammary glands of newborn boys require medication.
Cases are recorded in patients aged 11–15 years. As a rule, the breast increases due to the growth of adipose tissue. In persons of this age category, the disease is caused by physiological changes inherent in puberty and pathological processes in the body. 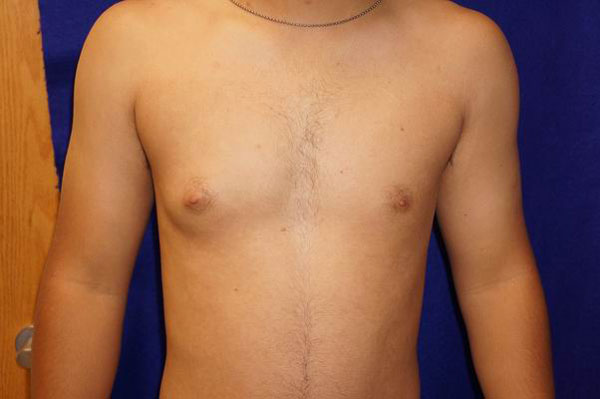
Signs of gynecomastia:
Violation of the ratio of hormones in the body is caused by changes in the work of the adrenal glands, which transform testosterone into estrogen. As a rule, the symptoms disappear on their own after a while, during which constant monitoring of the child's condition is required.
The appearance of signs of the disease in a boy who has not yet entered the phase of puberty indicates pathological changes in the endocrine system. In this case, an early examination and consultation with a specialist is recommended. 
In men after 30 years, the signs of the disease are differentiated depending on the characteristics of its course.
Often takes a diffuse form. It is characterized by the formation of seals up to 10 cm in size, inverted nipples and discharge from them.
Unilateral gynecomastia usually manifests itself as the formation of a dense nodule that does not cause pain. In some cases, this form of the disease precedes malignant neoplasms. 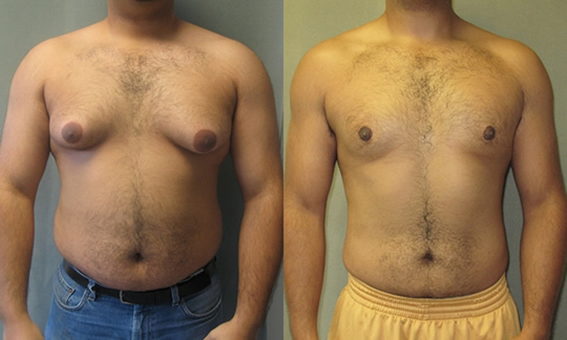
The increased content of prolactin in the male body complements gynecomastia with a number of other signs:
An increase in the content of female sex hormones leads to the appearance of the following symptoms in a patient with gynecomastia:

The danger is a change in the shape and swelling of the testicles in men. In this situation, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Gynecomastia in men is a fairly common disease. If changes occur in the mammary glands, it is necessary to consult a specialist, since in an advanced form the disease can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
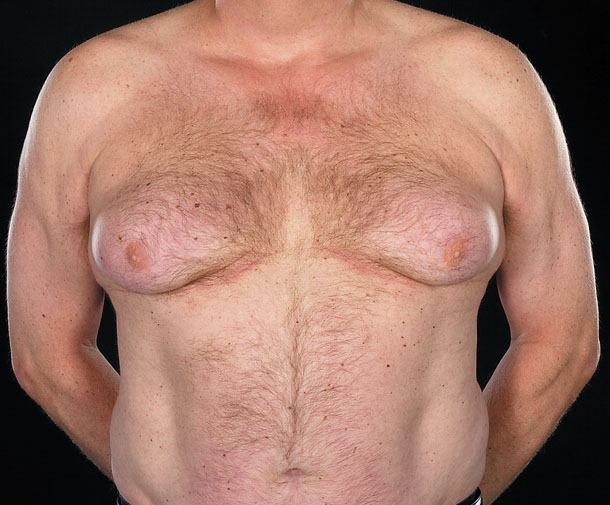
Gynecomastia is very common in boys and men. It is found in 45-75% of healthy adolescent boys and young men, in 40% of middle-aged and young men and in 70% of the elderly, causing them psychological discomfort, and sometimes physical inconvenience.
You will be interested to read:
This term is not used for an independent disease. It combines a multi-causal complex of symptoms (syndrome), which is manifested by the increased size of one or both mammary glands. Their intrauterine laying and maturation occur regardless of gender. In the pubertal period, the formation of the mammary glands in young men stops.
In men, the mammary glands are a rudimentary organ that has lost its original purpose in the course of evolutionary development. They consist of adipose tissue, a small amount of glandular tissue with ducts, the nipple and areola.
The development of glandular tissue and ducts, as well as their functioning, depend mainly on estrogen (female sex hormones) and progesterone, as well as on prolactin (pituitary hormone), which stimulates the formation of estrogen-sensitive receptors in the mammary glands.
Androgens (male sex hormones) are synthesized in the testicles and adrenal glands. In the peripheral tissue, predominantly adipose, under the influence of the aromatase enzyme, they are partially transformed into female sex hormones. In the liver cells, estrogens undergo rapid destruction due to the combination with sulfur and glucuronic acid and are excreted by the kidneys. In the male body, estrogens normally make up an insignificant fraction (0.001%) of the content of androgens - testosterone and its more active form dihydrotestosterone.
Under the influence of certain factors, the ratio of sex hormones changes in favor of estrogens, as a result of which changes in the mammary glands corresponding to the syndrome occur. The main causes of gynecomastia are as follows:
Gynecomastia in men is manifested by the growth in one or both mammary glands of adipose or glandular tissue. Tissue changes can be diffuse (evenly distributed) or nodular. Symptoms depend on the stage of the process:
The development of the syndrome is accompanied by an increase in the size of not only the breast, but also the nipples. In this case, there is a feeling of swelling, some compaction in the gland, determined by palpation, and sometimes soreness even when touched by clothing, but more often - a feeling of squeezing, heaviness and discomfort.
Gynecomastia can occur in the form of a diffuse enlargement of the glands or limited tissue compaction. Elastic seal with a diameter of 2 to 15 cm and a weight of up to 150 gr. is determined by probing, as a rule, in the nipple area. It has blurred contours, is not "soldered" with the surrounding tissue, smooth or "grainy". Sometimes there is an increase in pigmentation of the areola, which becomes darker. In rare cases, when pressing on the nipple, a white or clear discharge appears. If it contains an admixture of blood, has a dirty appearance, and is accompanied by an increase in axillary lymph nodes and/or their soreness, this may be a sign of a malignant neoplasm.
During the formation of nodular gynecomastia during palpation, a painless dense movable node with clear boundaries is determined, located in only one mammary gland. Most often, it is determined by an accidental examination by a doctor or by the patient himself.
Thus, in the clinical diagnostic aspect, gynecomastia is considered as:
The classification of the syndrome is based on the causes of imbalance in the male body of male and female sex hormones. The versatility and complexity of the mechanisms that regulate the hormonal state of the body determines the multiplicity of causes for the development of gynecomastia syndrome in men in different life periods, as well as its physiological or pathological nature. Depending on them, gynecomastia is distinguished:
It is not a sign of any pathological processes and is divided into gynecomastia:
Enlargement of the glands to a greater or lesser extent occurs in half of the boys during the first month after birth and disappears on its own over the next few months with breastfeeding or even weeks artificial feeding. There are two hypotheses about the reasons for this phenomenon:
Juvenile gynecomastia, the cause of which is not entirely clear, appears during the 3rd - 4th stage of puberty. In most adolescents, it manifests itself as symmetrical, and in some unilateral enlargement of the mammary glands in the form of swelling, heterogeneous and painful on palpation. Sometimes during this period, visually, the glands of boys differ little from the mammary glands of girls.
Some endocrinologists explain these changes by increased secretion of estrogens, androgens and pituitary gonadotropic hormones, associated with the still unstable functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. Other scientists associate teenage gynecomastia with excessive transformation of androgens into female sex hormones under the influence of increased activity of the aromatase enzyme.
Gynecomastia of mature and old age is due mainly to a decrease in androgen production.
Conditionally distinguish:
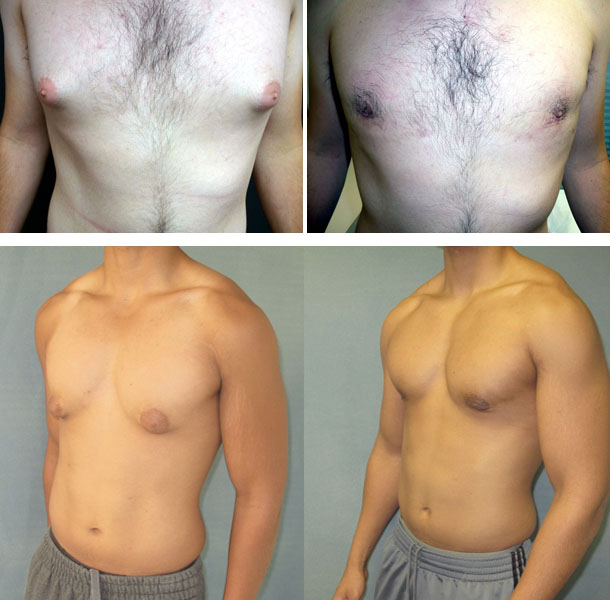
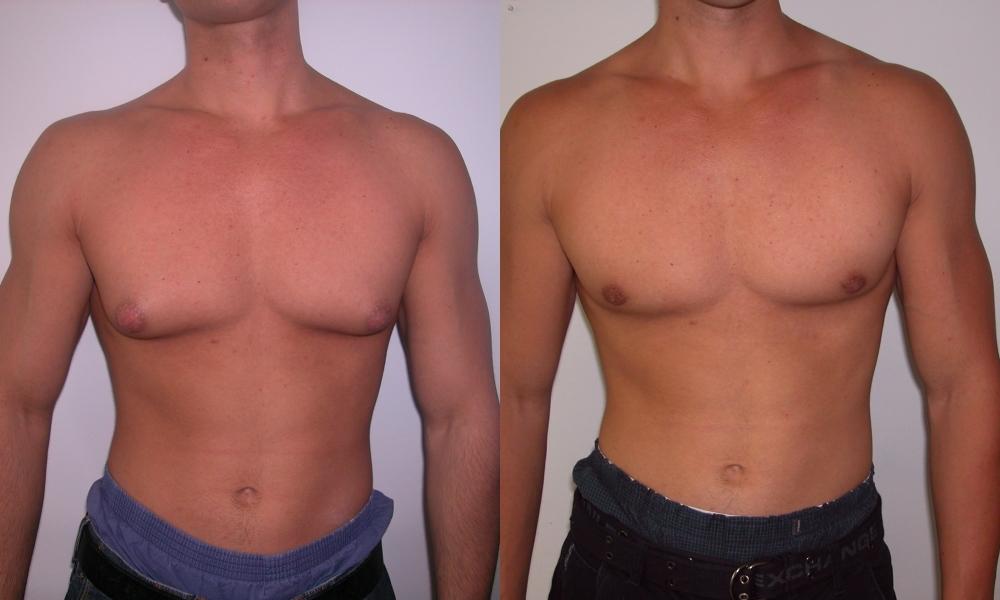
Surgical treatment of gynecomastia
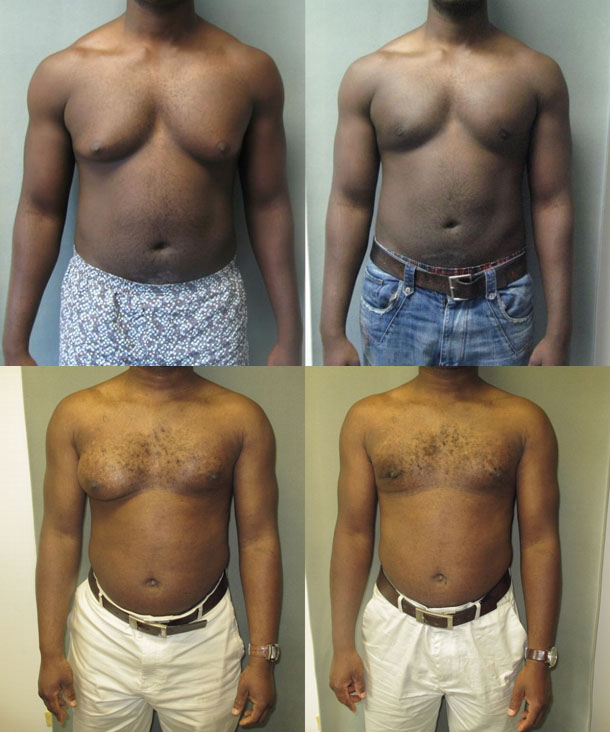
Lipomatous gynecomastia is not a consequence of hormonal disorders and is an accumulation of fat in both (rarely in one) mammary glands with general obesity of a constitutional-exogenous nature. With this form, the glands are mobile during palpation and physical movements, have a soft doughy texture, are painless, and the nipple-areolar complex is omitted. Sometimes with a slight general obesity, false gynecomastia can be significantly pronounced.
The reason for such obesity and, accordingly, the deposition of fat in the mammary glands is the absolute or relative deficiency of the peptide hormone leptin, produced in adipose tissues. Its function is to suppress hunger and enhance metabolic processes, which increase energy consumption and heat transfer.
In addition, abdominal fat contained in the abdominal cavity is currently considered as an endocrine organ in which various biologically active substances are synthesized, including estrogens, which contribute to female-type obesity. This form is referred to as false mixed gynecomastia.
Some authors also refer to mixed-type gynecomastia as changes that occur with obesity associated with dysregulation of the function of the adrenal cortex by the hypothalamus (hypotolamic syndrome) in adolescent boys. The cause may be trauma to the skull during or after childbirth, inflammatory or congenital diseases leading to increased CSF (intracranial) pressure.
It is a consequence of other diseases or external causes, in which there may be an excess of estrogen, an absolute or relative deficiency of androgens, a violation of the transformation of the latter into estrogens.
The main of these reasons are:
If necessary, conservative treatment is applied, and in some cases, removal of gynecomastia.
Physiological gynecomastia usually resolves on its own and does not require therapeutic correction. Only a psychological impact on adolescents is needed to prevent their feelings of inferiority, as well as dynamic monitoring in order to timely prevent the development of inflammatory processes in the mammary glands or malignant neoplasms.
Treatment of gynecomastia of the idiopathic form before the appearance of signs of fibrotic changes is possible with the help of Clomiphene, Tamoxifen (suppresses estrogens) - 10 mg 2 times a day for 2 months. After that, it is canceled and, in the absence of effect, the administration of Testoplakton, which blocks aromatase activity, is prescribed. However, the effectiveness of these drugs in the absence of endocrine disorders is questionable.
The term gynecomastia means a syndrome (a set of specific symptoms), which is manifested primarily by an increase in the volume of the mammary glands (one or both). In the representatives of the stronger sex, this health problem occurs quite often - at least 40-70% in boys and adolescents, 40% in young and mature men, 70% in the elderly. Symptoms do not always cause physical discomfort or pose a danger (if we are talking about the so-called false condition), however, in almost 100% of cases, breast augmentation is the cause of psychological problems, and this is already a reason to get rid of this syndrome in time.
The mammary glands, as part of the human body, are laid down during the period of intrauterine maturation of the fetus. Already after the birth of a child, they continue to develop until the onset of puberty in boys, when the process of formation of this organ, which is rudimentary for the representatives of the stronger sex, is completed. The male mammary glands are formed mainly by adipose tissue, to a lesser extent - glandular tissue with ducts, the latter developing and functioning with the active participation of the female sex hormones estrogen.
In a healthy male body, the proportion of these substances is negligible, since they are broken down and excreted in a timely manner, without accumulating in the tissues. With a combination of certain reasons, the volume of female sex hormones increases abnormally, which leads to pathological changes affecting the mammary glands. In particular, there is an overgrowth of the tissues forming the organ (adipose, glandular, or both at once), which is diffuse in nature with a uniform distribution or manifests itself in separate nodes.
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS by an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result is 100% - complete elimination of prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. ACTIVE METHOD.

From the point of view of danger, for health and life, gynecomastia in men is classified into several groups:
It is recommended to pay close attention to the second and fourth points, since similar signs of gynecomastia noticed in time will help to avoid serious violations of the health and life of a man. For example, a pathological enlargement of the male mammary glands can be a symptom of:
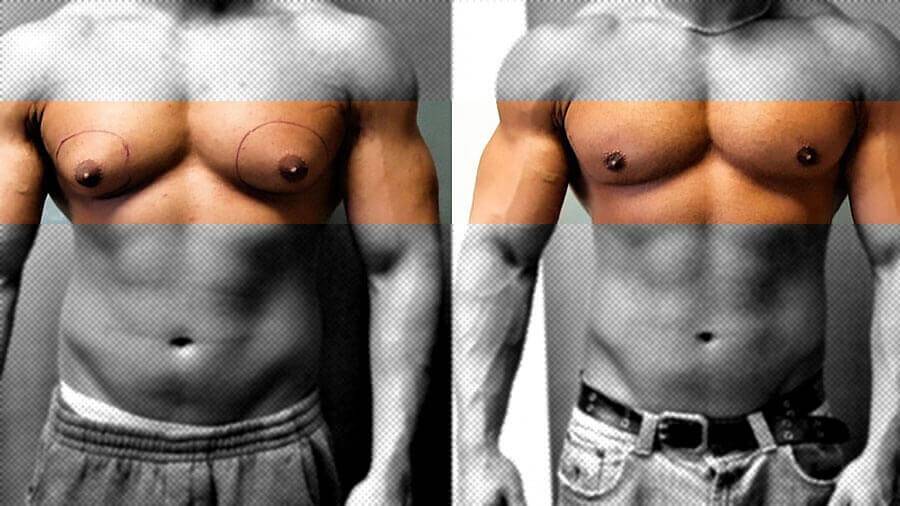
A male body with gynecomastia, which is an independent symptom of various health problems, can be called a time bomb: most of the diseases that cause this condition are so serious that the patient may begin to fear for his life, unless, of course, he asks for medical help. And this is not to mention the fact that the pathological enlargement of the mammary glands itself can turn into malignant neoplasms and develop into breast cancer.
Experts identify the following developmental symptoms and symptoms due to the growth and compaction of the fatty and glandular tissues that form the mammary glands:
If we are talking about the form of the disease that is provided by a drop in the level of the hormone prolactin in the blood, the characteristic symptoms can be supplemented by such manifestations as:
Problems with sexual desire and the physical ability of a man to have sex (and, accordingly, it is logical to complete them) are also a symptom of gynecomastia, caused by problems with the level of male and female sex hormones. If the content of estrogen is seriously increased in the blood of a man and there is practically no testosterone, this leads to the pathology of the growth of fatty and glandular tissues of the mammary glands and the failure of libido. In addition, if a man suffers from an increased level of female sex hormones, this is also noticeable due to:
Even if these manifestations are not associated with gynecomastia, they are still sufficient reason for a man to see a doctor and undergo a medical examination. It is all the more important to visit a specialist if all the signs indicate a high probability of a malignant neoplasm:

Unilateral breast augmentation may indicate the likelihood of a malignant neoplasm
Manifestations of all these symptoms occur and progress in accordance with the stages of development of the disease as a whole. As the disease progresses, the affected mammary glands (the area around the nipple) will be able to reach a size of at least 10-15 cm, the areola around them will expand and become pigmented. In general, the pathological proliferation of tissues that form the mammary glands in men proceeds in 3 stages:
Among other signs of the development of the disease, experts call:
Important: with gynecomastia, characteristic manifestations can be noticeable on both mammary glands, although most often gynecomastia manifests itself unilaterally, usually on the left.
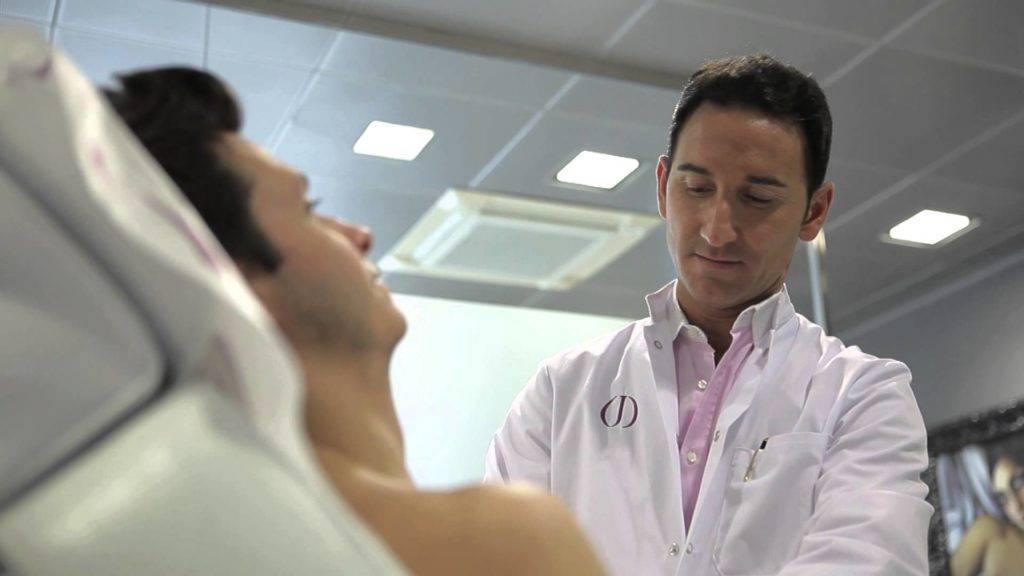
The patient is examined and palpated
Men who find themselves with problems with swelling or soreness of the breast (in the area of the nipples and their areolas) should seek medical help. The diagnostics assigned by him will allow to identify the disease in a timely manner and determine whether changes in the structure of breast tissues are pathological (that is, whether they are gynecomastia) or are one of the symptoms of an unhealthy lifestyle (nutrition or beer abuse).
The patient who turned to the doctor will have to undergo a number of medical examinations, and first of all, inspection and palpation of suspicious areas. Palpation (palpation by hand) is a method of physical examination, during which the main symptoms of gynecomastia are revealed - the presence of seals and enlargement of the breast, pain when touched or the absence of it, the presence and absence of secretory discharge from the nipple. Usually, palpation reveals formations-seals 1-10 cm in size, localized in both or only one mammary gland, which makes the breast asymmetric.
Also, the following procedures will be assigned to the man:
Before finally determining gynecomastia, specialists will send a man additionally for testing. As part of laboratory diagnostics, doctors, among other things, will determine the level of hormones in his blood. The presence and quantity is usually considered:
If there is a suspicion that gynecomastia itself is a symptom of the disease, the patient is sent for an ultrasound of the testicles and CT of the adrenal glands. And in any case, a sick man will have to get advice from individual specialists - a urologist, endocrinologist, oncologist, therapist and surgeon.
The process of detecting gynecomastia in a man is a series of detailed examinations of the patient, allowing to establish an accurate diagnosis and present a complete clinical picture of the disease (including the causes and factors of its occurrence). High-quality diagnostics gives doctors (usually an oncologist and a surgeon) the opportunity to assess the nature of the lesion of the mammary glands in each case, to detect the stage of its development, variety, and also to examine the body as a whole.
Depending on what the diagnostic results show, as well as in accordance with the identified form of gynecomastia (true, false, physiological or pathological), appropriate treatment will be prescribed. If the development of seals is detected on time, in order to get rid of the problem, the patient will have, for example, to “sit” on a course of hormonal drugs, and if treatment is started at the last stage, surgical intervention is indispensable.
The symptoms of gynecomastia are quite noticeable for those who closely monitor their health. The mammary glands become swollen and heavy, the breasts feel painful when touched, problems with potency (with the most common form of the disease) and sexual function in general begin - this is enough to go to a doctor's consultation. Moreover, the symptoms of gynecomastia do not always mean only this lesion - they can also represent a whole range of symptoms indicating even more complex malfunctions in the body of a man.
Do you have PROSTATITIS? Have you already tried many remedies and nothing helped? These symptoms are familiar to you firsthand:
As world statistics show, the number of men suffering from a pathology called gynecomastia last decade has increased significantly. There are many reasons for this, and sometimes it becomes very problematic to establish the exact factor that provoked the development of pathology in any particular case. So what is gynecomastia? How does it manifest itself, what effective prevention of this disease exists? And is it possible to recover from this disease? This and much more will now be discussed.
What is gynecomastia in a man and what kind of discomfort does it bring? Translated from Greek, the term "gynecomastia" means "breast" and "woman". In other words, this disease is characterized by a violation of the hormonal background in the body, as a result of which men have an increase in the mammary glands according to the female type.
Gynecomastia (ICD diagnosis code: No. 62) can develop at any age. Most often, it is diagnosed in men aged 50-60 years against the background of age-related changes in the body, accompanied by hormonal disorders. However, in some cases, signs of pathology - gynecomastia - also appear in young men. And there are several reasons for this. But before talking about them, it should be noted that this disease can be of several types:
True gynecomastia is characterized by the growth of the glandular or connective components of the mammary gland, which causes a significant increase in its volume (up to 20 cm). In their structure, the glandular and connective tissues are dense, and therefore, in the treatment of this problem, it is impossible to resort, so to speak, to conventional liposuction. It won't give any results. This requires a more complex operation.
True gynecomastia also has its own varieties. She happens:
True gynecomastia of the physiological type occurs mainly in men over 50 years of age. It does not require special treatment. And, according to doctors, the appearance of this pathology in men at this age is an absolute norm, since it is at this age period strong hormonal surges occur in the body.
True pathological gynecomastia in adult men is already considered a serious disease that requires immediate treatment. Its development occurs as a result of a violation of the physiological hormonal balance, and may be the result of long-term use of certain drugs.

Pathology can occur due to the use of certain drugs
With the development of false gynecomastia, the adipose tissue of the mammary glands grows. It occurs most often in obese men. In this case, the treatment includes two stages at once - pumping out excess fat from the gland (liposuction is performed) and eliminating the cause of excess weight (normalization of metabolism, lifestyle changes, etc.).
There is another type of this pathology - mixed gynecomastia. It is characterized by the simultaneous growth of all structures of the mammary glands at once (fatty, glandular and structural tissues). Pathological tissue growth can be both unilateral and bilateral. In men, unilateral gynecomastia is extremely rare. Most often, this disease affects two mammary glands at once.
Considering such a topic as gynecomastia in men and the causes of its occurrence, it should be noted that the main reason for the development of this pathology is a disturbed hormonal balance, in which the male body has an active production of female hormones - estrogens.
The following conditions and diseases can lead to this problem:
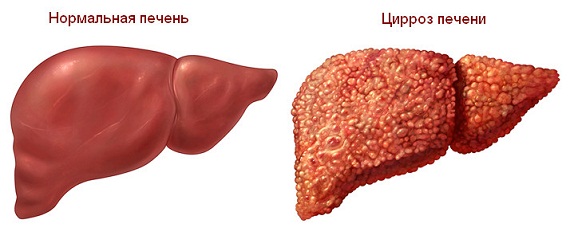
The causes of gynecomastia may be hidden in the impaired functioning of the liver as a result of the development of cirrhosis and degeneration of its tissues. In addition, breast enlargement in men is often the result of taking various dietary supplements that are taken by many athletes in order to quickly gain muscle mass.
Drugs such as Reserpine, Phenothiazine, and Spironolactone can also cause gynecomastia when taken long-term. The reason for the development of this pathology may still be hidden in the excessive use of alcoholic beverages and drugs.
Gynecomastia can occur due to disorders in the liver
Looking at gynecomastia in photos and videos, you can see that the mammary glands of a man are significantly enlarged and look more like women than men. However, in addition to the visual change in the shape of the breast, patients are also concerned about other symptoms of this pathology. Among them:
The last symptoms of gynecomastia in men are associated with the active production of estrogen in the body. For the same reason, engorgement and compaction of the mammary glands occur, as well as an increase in the size of the areola and a change in their color - they become darker (with the development of gynecomastia in men in the photo, this symptom is visible to the naked eye).
And if we talk about how to determine gynecomastia in men, then it should be noted that visual examination alone and the detection of sexual activity disorders is not enough. A thorough examination of the chest is required.
On palpation of the chest, compacted areas can be noted, which, in addition to feeling heaviness, do not cause any discomfort in the man (there is no pain). If you press on the nipple, you can see a clear-colored discharge similar to colostrum, which makes it clear that the patient has serious health problems that require immediate treatment.
With gynecomastia, the symptoms can be of a different nature, and they depend, first of all, on the degree of development of pathological processes in the breast. In total, there are 3 degrees of breast enlargement in men:
Every man should understand that the presence of this problem can lead not only to the appearance of complexes about the appearance, but also cause serious problems in the genital area, up to impotence. Therefore, if a man began to notice the first signs of gynecomastia (discharge from the nipples, engorgement of the glands, etc.), he should immediately consult a doctor. The sooner a problem is identified, the easier it will be to fix it.
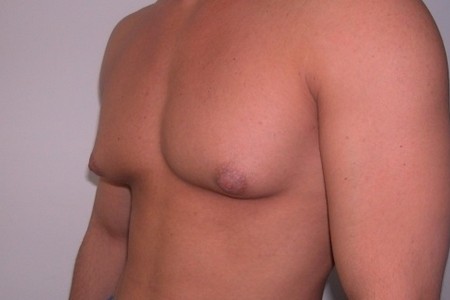
In the first stage of the disease, the volume of the breast does not exceed 6 centimeters
However, examination alone is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. With the development of gynecomastia in a man, the diagnosis should also include:
The most informative diagnostic method is ultrasound, in which not only the mammary glands are viewed, but also the axillary lymph nodes, as well as the testicles. Thanks to this study, the doctor can determine the type of gynecomastia (false, true, mixed, etc.), as well as the degree of development of pathological processes in the tissues of the mammary glands and the cause of their occurrence.
Laboratory blood tests are aimed at determining the level of:
Important! In the event that an elevated level of estradiol and hCG was detected during a laboratory blood test, the patient should immediately be examined for malignant tumors! For this, diagnostic methods such as a blood test for the CA-125 tumor marker, CT and MRI can be used.
If during the examination of a man for gynecomastia, the causes of the development of the pathology were also established (for example, hypothyroidism, obesity, etc.), additional consultations of narrow specialists - an oncologist, endocrinologist, urologist, etc.
It is difficult to answer specifically the question of how to get rid of gynecomastia, since each case requires an individual approach. Here it is necessary to accurately determine the type of pathology and establish the reason why there is an increase in the mammary glands in a man.
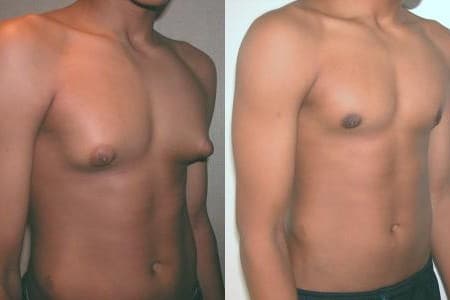
Treatment of gynecomastia in each case is determined individually.
So, for example, gynecomastia of a physiological type, which begins to form during fetal development, does not require any treatment and disappears on its own within a few months.
Pathological gynecomastia in men is usually treated with hormone therapy, the purpose of which is to suppress the production of estrogen in the male body and increase testosterone synthesis.
Hormone therapy most often occurs with the use of drugs such as:
Important! You can not take hormonal drugs without a doctor's prescription! Their uncontrolled intake can lead to serious health problems and provoke the progression of pathology!
In the event that taking hormone-containing drugs does not give positive dynamics and there is a further increase in breast volume, surgical intervention is performed. What it will be, the doctor decides, taking into account the type of gynecomastia.
In the event that the patient has a true or mixed form of the disease, a mastectomy is performed. This type of surgery is the most effective for gynecomastia, and its price depends not only on the area in which the clinic is located, but also on the scale of the pathological processes.
In the case of false gynecomastia, in which there is an excessive growth of adipose tissue in the mammary glands, liposuction is used, during which excess fat is removed from the affected area using special tools.
But it should be noted that if, after liposuction, the therapeutic measures prescribed by the doctor are not carried out, the symptoms of gynecomastia may reappear after a while.
Therefore, it is very important that gynecomastia prophylaxis is carried out after treatment, which includes several simple rules – proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, moderate physical activity, etc.
And most importantly, in no case should you self-medicate! To prevent the occurrence of this problem again, even a banal sore throat should be treated under the strict supervision of a physician. After all, as mentioned above, there are some drugs that can easily provoke breast enlargement in men, as a result of which the entire treatment process will have to be repeated again.